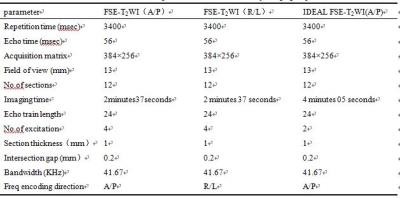
2570
High‑resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Basilar Artery with Iterative Decomposition of Water and Fat with Echo Asymmetric and Least-squares Estimation(IDEAL): A Feasibility Study1Radiology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, People's Republic of China, 2GE healthcare China, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
To explore the potential for high-resolution MR imaging using IDEAL FSE-T2WI as compared to FSE-T2WI in the assessment of the basilar artery wall. High-resolution FSE(A/P), FSE(R/L) and IDEAL FSE(A/P) T2W images were acquired from basilar artery of 30 patients using a 3.0T MRI scanner.The threeimage sets were evaluated for overall image quality and graded using a 4-point Likert scale.IDEAL FSE-T2WI (A/P) scores is higher than FSE-T2WI (A/P) and FSE-T2WI (R/L).FSE-T2WI (A/P), FSE-T2WI (R/L) andIDEAL FSE-T2WI (A/P) difference with statistical significance,respectively.IDEAL FSE-T2WI images showed improved image quality compared to FSE-T2WI technique at 3T.
ZHANG Yu1,ZHA Yun-fei1,LI Liang1,HU Lei1, Wu Bing2, Lin Hui2.
1、Department of Radiology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University,Wuhan 430060,China
2 GE healthcare China
Purpose Intracranial atherosclerosis is a major cause of ischemic stroke, accounting for about 30-50% of the patient population1. The vertebral basilar artery is a predilection site of cerebral atherosclerosis. High resolution magnetic resonance imaging has been widely used in intracranial artery plaque imaging due to its non-invasiveness and superior soft-tissue contrast. Fast spin echo (FSE) is sensitive to magnetic susceptibility artifacts that may lead to image distortion and signal loss along the frequency encoding direction. Susceptibility artifacts between brain and bone in the skull base may result in the loss of signal in the basilar artery(BA) wall and hence affect the diagnosis of plaque, especially in the patients with high degree of gasification of the sphenoid sinus. Iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetric and least-squares estimation (IDEAL) has the potential of reducing the susceptibility artifacts. In this work, we study the use of IDEALin depicting basal artery wall and compare the results to conventional FSE-T2WI with different frequency encoding directions.
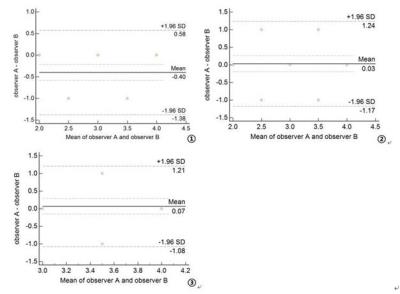
Methods A total of 30 patients with high degree of gasification of the sphenoid sinus (17 males and 13 females, age:51.9 ± 16.5) were enrolled in this ethic committee approved study. All the participants underwent MR exams consisting of IDEAL FSE-T2WI and conventional FSE-T2WI, and the detailed scan parameters are shown in Table 1. Frequency encoding direction was set to beanterior-posterior in IDEAL, whereas for FSE-T2WI, both anterior-posterior and right-left directions were used. Images were evaluated using a 4-point Likert scale (1, nondiagnostic; 4, outstanding).Bland-Altman analysis was used to analyze the consistency of image quality score of two observers(95% LOA).The data were analyzed by SPSS 17.0 statistical software, and the samples were compared by non-parametric statistics. The results were compared with the Wilcoxon paired sign rank test, and the results were compared by the Friedman test. P <0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
Results A typical set of images from the three acquisitions is shown in Fig.1. The results of consistency test are shown in Fig.2. It is seen that the difference of the quality grading of basal artery images obtained was within the 95% consistency interval, and the two observers showed good consistency. The differences of the three groups were statistically significant (P <0.001).The total scores for FSE-T2WI (A/P), FSE-T2WI (R/L) and IDEAL FSE-T2WI (A/P) images, respectively, were as follows:81, 92 and 115. Statistically significant difference was observed between FSE-T2WI (A/P) and FSE-T2WI (R/L) (Z=-3.317,P=0.001); between FSE-T2WI (R/L) and IDEAL FSE-T2WI (A/P) (Z=-4.600,P=0.000); and between FSE-T2WI (A/P) and IDEAL FSE-T2WI (A/P) (Z=-4.540,P=0.000).
Discussion It is seen in this study that IDEAL FSE-T2WI (A/P) is advantageous to FSE-T2WI using A/P or R/L as frequency directions with the presence of susceptibility artifacts. Although FSE-T2WI is mostly commonly used for imaging of cerebral arteries due to its high SNR and short imaging time, it may feature image distortion and signal loss in sellar-type sphenoidal sinus region. The IDEAL technique uses a three-point Dixon method that separates the fat content in the tissue while corrects the phase shift caused by susceptibility induced dephasing. With a proper choice of scan parameters, high level of SNR can be maintained that lead to improved the detection of intracranial plaque and features of the display2. It hence can be concluded that IDEAL FSE may be of great clinical value in displaying basilar arteries.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Yunfei ZHA professor and study participants for their help and participation on this study.References
[1]Yu J H, Kwak H S, Chung G H, et al. Association of Intraplaque Hemorrhage and Acute Infarction in Patients With Basilar Artery Plaque[J]. Stroke,2015,46(10):2768-2772.
[2] Reeder S B, Pineda A R, Wen Z, et al. Iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation (IDEAL): application with fast spin-echo imaging[J]. Magn Reson Med,2005,54(3):636-644.
Figures