2546
New Enhancing and Chronic Multiple Sclerosis Lesions measured on Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping and Diffusion-Weighted ImagingYihao Yao1 and Yi Wang2,3
1Department of Radiology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science & Technology, Wuhan, People's Republic of China, 2Department of Radiology, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY, United States, 3Biomedical Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, United States
Synopsis
QSM and DWI are sensitive to changes in MS lesions at various ages. We found chronic MS lesions had higher relative susceptibilities and lower relative ADC values as compared to new enhanced lesions. Combining QSM and ADC measurements could differentiate each two subtypes in four subtypes of lesions (nodular/shell enhanced lesions, rim+/- lesions). The pattern of QSM and ADC findings suggests that shell enhanced lesions have more demyelination than nodular enhanced lesions and rim- lesions. Combining QSM and ADC measurements might be a better way to differentiate MS lesions at various ages and provide more information of micro-changes of lesion.
Purpose
To assess new enhanced and chronic multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions by using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI).Background
QSM provides an effective means to directly map the distribution of susceptibility sources including iron and demyelination1. QSM is sensitive to changes in MS lesions at various ages. Susceptibilities of MS lesions increased from similar susceptibility values to NAWM in acute enhanced stage to significantly higher susceptibilities than NAWM in early to intermediate nonenhanced stage, and then back to susceptibility values similar to NAWM in chronic nonenhanced stage2. DWI of MS lesions also show different kinds of signal as time going on. Prominent apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) reduction, normalization (or pseudonormalization), elevation can be seen at superacute nonenhanced stage, early enhanced stage, late enhanced stage to early nonenhanced stage, respectively3. ADC variations at the chronic nonenhanced stage have yet to be studied.Methods
Retrospecitively selected 32 clinically confirmed MS patients (20 patients with 52 new enhanced lesions, 12 patients with 53 chronic lesions ≥6 years). QSM were reconstructed from gradient-echo images. DWI maps were used to reconstruct ADC maps. New enhanced lesions were divided into two subtypes as nodular enhanced lesion and shell enhanced lesion by different enhanced patterns. Among chronic lesions, rim positive (rim+) lesions and rim negative (rim-) lesions were identified on QSM. QSM and ADC measurements for MS lesions were calculated by using a ROI semi-automatic software ITK-SNAP. The lesion ROIs were placed on T2w images and then were overlaid on QSM and ADC with manual adjustment as required. ROIs as normal appearing white matter (NAWM) reference were drawn on the contralateral mirror site of the lesions with similar shape and size. New enhanced lesions were compared to chronic lesions by using t test. Comparisons between four subgroups were done by ANOVA.Results
Chronic lesions (10.91±13.66) had a relatively higher susceptibility as compared to new enhanced lesions (3.54±6.16) (p=0.001). The relative ADC values of chronic lesions (278.24±169.96) were lower as compared to new enhanced lesions (378.34±161.59) (p=0.003) (Fig 1). Relative susceptibilities and ADC values for nodular enhanced, shell enhanced, rim- and rim+ MS lesions were shown in (table 1). Statistical comparison of relative susceptibility and ADC values from four subgroups of lesions were shown in (table 2) and (table 3).Discussion and conclusions
Our results establish that chronic MS lesions had higher relative susceptibilities and lower relative ADC values as compared to new enhanced lesions. Combining QSM and ADC measurements could differentiate each two subtypes in the four subtypes of lesions (nodular enhanced lesions, shell enhanced lesions, rim+ lesions and rim- lesions). The increase of relative ADC values is thought to reflect expanded extracellular space, even though the individual contributions from edema, demyelination, and axonal loss are yet unknown. The pattern of QSM and ADC findings suggests that shell enhanced lesions have more demyelination than nodular enhanced lesions and rim- lesions. Combining QSM and ADC measurements might be a better way to differentiate MS lesions at various ages and provide more information of micro-changes of lesion tissues without using contrast enhanced agent. More specific studies are needed to do with myelin water fraction which is a well- validated MRI biomarker of myelination4.Acknowledgements
We are acknowledged support from grants: R01NS072370, R01NS090464, R01NS095562.References
1. Wang Y, Liu T. Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM): Decoding MRI data for a tissue magnetic biomarker. Magnetic resonance in medicine : official journal of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine / Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 2015;73:82-101 2. Chen W, Gauthier S, Gupta A, et al. Dynamic magnetic property of multiple sclerosis lesions at various ages measured by quantitative susceptibility mapping. ISMRM. Salt Lake City, USA; 2013 0692 3. Eisele P, Szabo K, Griebe M, et al. Reduced diffusion in a subset of acute MS lesions: a serial multiparametric MRI study. AJNR American journal of neuroradiology 2012;33:1369-1373 4. Laule C, Leung E, Lis DK, et al. Myelin water imaging in multiple sclerosis: quantitative correlations with histopathology. Multiple sclerosis 2006;12:747-753Figures
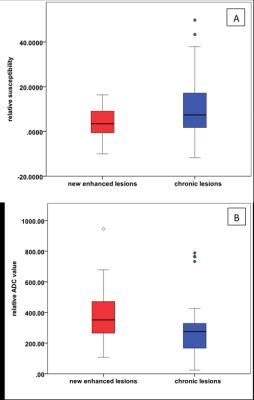
Fig 1. Chronic lesions had a higher relative susceptibility
and lower relative ADC value as compared to new enhanced lesions.
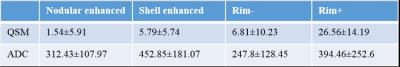
Table 1.
Mean
relative susceptibilities and relative ADC values of four subtypes of lesions.
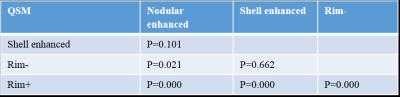
Table 2. P values of relative susceptibility comparisons
between each two of the four subtypes of lesions.
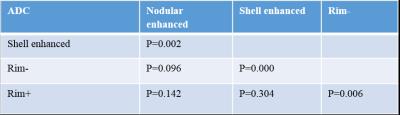
Table 3. P values of relative ADC value comparisons between
each two of the four subtypes of lesions.