2301
The effect of the dopamine D4 receptor −616 C/G polymorphism on gray matter volume and functional connectivity in pediatric primary nocturnal enuresis patients1Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, People's Republic of China, 2Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, 3Philips healthcare
Synopsis
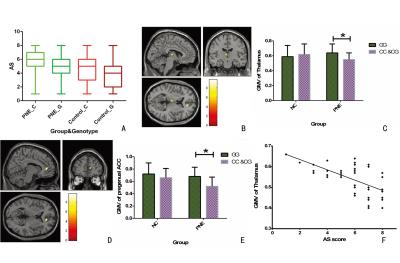
The study assessed the effects of (DRD4) -616 (rs747302) gene variation on gray matter volume (GMV) and arousal from sleep (AS) scores in children that suffered from primary nocturnal enuresis (PNE) and normal controls and found that The −616 C/G SNP in the DRD4 promoter may affect the AS scores and GMV in the thalamus and pregenual ACC in PNE children.
PURPOSE
The dopamine D4 receptor (DRD4) promoter (-616; rs747302) has been associated with primary nocturnal enuresis (PNE), however its relationship between neuroimaging have not been investigated. Therefore, we assessed the effects of the DRD4 -616 C/G single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) on the gray matter volume (GMV) and resting-state functional connectivity (rsFC) in PNE children using voxel-based morphometry (VBM) and resting-state fMRI methods.METHODS
Genomic and imaging data were obtained from 83 PNE children and 86 healthy controls. DRD4 -616C/G was genotyped. Arousal from sleep (AS) was assessed on a scale of 1-8. Both the main effect of genotype and the group (PNE/control)-by-genotype interaction on GMV and FC were calculated.RESULTS
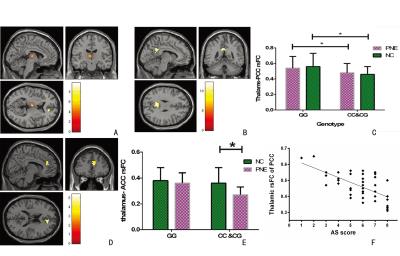
The AS scores of C-allele carrying PNE children were higher than that of GG homozygotes. Group-genotype interactions of GMV were found in the thalamus and pregenual anterior cingulate cortex (ACC). Post-hoc testing revealed C-allele carriers had a decreased GMV in the thalamus and pregenual ACC than GG homozygotes in PNE group. The GMV of the thalamus also correlated with AS in them. The GMV abnormal area in the thalamus were chosen as the seed ROI for FC analysis. The main effect of genotype to thalamic FC was shown in the posterior cingulate cortex (PCC). The Z values of thalamic FC in the PCC also correlated with the AS scores in C-allele carrying PNE children.RESULTSDISCUSSION
A difficulty in arousal from sleep is a prerequisite for PNE, and has been proven in PNE patients through questionnaires, auditory signals and electroencephalographic analysis1. We speculate that the C allele may disrupt the activator protein 2 (AP-2) binding site in the promoter region of the DRD4 gene. Since AP-2 is a sequence specific mammalian transcription factor that can activate gene transcription 2, the mutation may lead to a down regulation of DRD4 transcription. Consequently, the decrease of dopamine D4 receptors may weaken the inhibition of depolarization-evoked by Ca2+-dependent γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) release, causing increased GABA concentrations in the brain 3,4.
Other studies have indicated that the majority of the sleep ‘active’ and sleep ‘inactive’ neurons are located in pregenual ACC, suggesting that the pregenual ACC is the central hub in the functional architecture of the mPFC with regard to sleep cycle5.
The thalamus plays an important role in the switch between sleep and waking, relaying sensory afferent signals from the bladder and transmitting them through the periaqueductal gray, to the ACC, the insula, and the lateral prefrontal cortex . Several previous imaging studies have also shown that the strength of thalamo-cortical connectivity was closely related to vigilance and external conscious perception . The altered thalamic GMV may result in an inability to wake during sleep in response to the need to void, and this is consistent with abnormally large urine volume in the bladders of children with PNE.
Additionally, abnormal functional connectivitie between the thalamus and DMN in C-allele carrying PNE children were also oberved. An increasing number of results have suggested that the DMN plays a key role in generating conscious awareness, Therefore, the defects in thalamus-DMN connectivity may not allow the children carrying DRD4 −616 C allele to awaken in sleep, and make then more liable to nocturnal enuresis.
CONCLUSION
In summary, among PNE children, C-allele carriers of rs747302 were associated with a higher AS score and decreased GMV and FC in the thalamus and DMN. .Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Umlauf, M. G. & Chasens, E. R. Bedwetting--not always what it seems: a sign of sleep-disordered breathing in children. Journal for specialists in pediatric nursing : JSPN 8, 22-30 (2003).
2 Williams, T. & Tjian, R. Characterization of a dimerization motif in AP-2 and its function in heterologous DNA-binding proteins. Science 251, 1067-1071 (1991).
3 Floran, B., Floran, L., Erlij, D. & Aceves, J. Activation of dopamine D4 receptors modulates [3H]GABA release in slices of the rat thalamic reticular nucleus. Neuropharmacology 46, 497-503, doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2003.10.004 (2004).
4 Govindaiah, G., Wang, T., Gillette, M. U., Crandall, S. R. & Cox, C. L. Regulation of inhibitory synapses by presynaptic D(4) dopamine receptors in thalamus. Journal of neurophysiology 104, 2757-2765,
Figures