2261
Characterizing the Effect of Age on Measures of White Matter Integrity in the Optic Radiations of Children with and without Neurofibromatosis Type 11Pediatrics, University Hospitals Rainbow Babies & Children, Cleveland, OH, United States, 2Pediatrics, The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, 3Pediatric Neurology, The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, 4Radiology, The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
Synopsis
DTI measures in the optic radiations are a promising biomarker of vision in children with optic pathway gliomas, but normal values for fractional anisotropy (FA), radial diffusivity (RD), and mean diffusivity (MD) in young children have not been defined. In 40 children with neurofibromatosis type I (NF1) and 55 healthy control children between 0-14 years of age, we measured FA, RD and MD in the optic radiations. This study represents the first investigation of normal DTI measures in the optic radiations in young children and demonstrates an altered developmental trajectory in the optic radiations of children with NF1.
Purpose
As measures of white matter integrity are developed as imaging biomarkers, it is critically important to understand the effect of age and maturity on diffusion measures in different populations. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of the optic radiations has been investigated as a potential biomarker of vision in a variety of pathologies including optic neuritis,1 glaucoma,2 amblyopia,3 prematurity4 and optic pathway glioma.5 However, normal values for fractional anisotropy (FA), radial diffusivity (RD), and mean diffusivity (MD) of the optic radiations in young children have not been defined. Non-invasive measures of visual function are especially important in children who may have difficulty cooperating with standard assessments of vision, such as children with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) who are predisposed to optic pathway gliomas, cognitive challenges and attention deficit. This study sought to define normal values for diffusion measures of the optic radiations in children, and to determine if developmental trajectories differed between healthy controls and children with NF1.Methods
In a retrospective, cross-sectional study of 40 children with neurofibromatosis type I (NF1) and 55 healthy control children between 0-14 years of age who underwent diffusion imaging of the brain, we measured FA, RD and MD in the optic radiations. A review of medical records insured that subjects had no history of brain tumor, CNS surgery/biopsy, or prematurity less than 36 weeks gestational age. Subjects were excluded if they had a neurologic condition that may affect white matter integrity (including increased intracranial pressure, structural brain abnormality, epilepsy or multiple sclerosis), or ophthalmic disease that may affect visual acuity (amblyopia, cataract, glaucoma or retinopathy of prematurity).
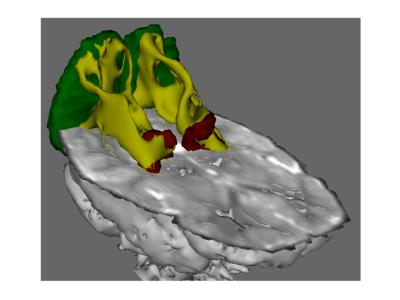
All MR examinations were performed at 3T on either a Trio, Skyra or Verio (Siemens; Erlangen, Germany). Diffusion MR was acquired with an echo planar pulse sequence with 128 x 128 matrix, in-plane voxel size of 2 x 2mm, diffusion weighting of b=1000 s/mm2, and full brain coverage with no gap between slices. Examinations were acquired with 30 gradient directions and 2mm slice thickness. On the 3T Trio, TE was 91-93ms, with TR of 7.3-11.6 s and bandwidth of 1395Hz/pixel. On the Skyra, TE was 84ms, with TR of 9.4-9.6 s and bandwidth of 1565Hz/pixel. On the Verio, TE was 91-104ms, with TR of 9.4-14 s and bandwidth of 1395Hz/pixel. Probabilistic tractography of the optic radiations was performed (FMRIB’s Diffusion Toolbox) using a previously described automated method6 between the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus and the occipital poles. (Figure 1).
Regression models of age, gender and NF1 status on DTI measures were considered (linear, exponential, logarithmic, quadratic). A likelihood ratio test was used to determine whether NF1 status and gender mediated the effect of age on DTI measures, and interaction terms between age and NF1 status were investigated (p<0.2 threshold of significance). 95% confidence interval of DTI measures were derived from the regression model.
Results
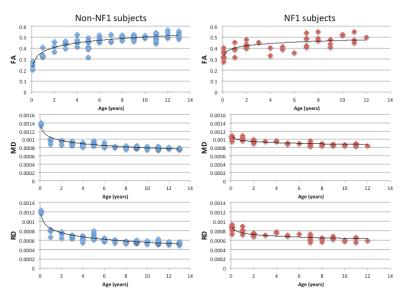
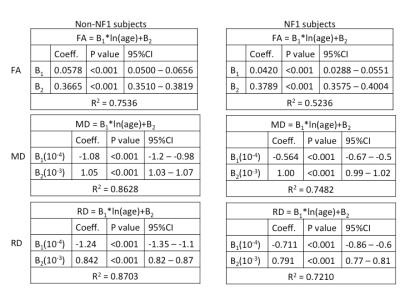
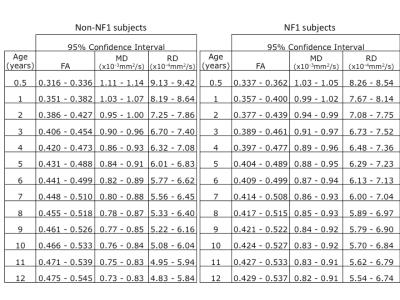
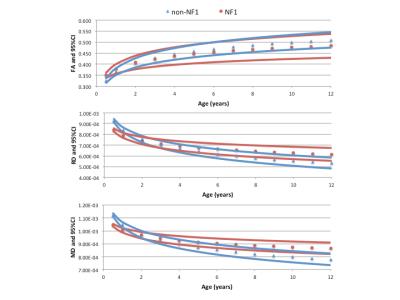
DTI measures of white matter integrity (FA, RD and MD) vs. age in subjects with and without NF1 are shown in Figure 2. The relationship between age and FA was non-linear and ln(age) was determined to be the best model (Table 1). While NF1 status was not a significant covariate in the model (p=0.743), NF1*ln(age) met the predetermined threshold for significance (p=0.073). Therefore, NF1 and non-NF1 subjects were modeled separately (Table 1). The derived models were used to calculate 95% confidence intervals for normal values of DTI measures from 0-12years (Table 2 and Figure 3).Discussion
DTI measures in the optic pathways vary with age as the optic pathways mature with age and development. Defining normal values for white matter integrity among children is essential to the continued development of DTI as a radiographic biomarker of vision. This study represents the first investigation of normal DTI measures in the optic radiations in young children and demonstrates altered developmental trajectory in the optic radiations of children with NF1.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Neurofibromatosis Therapeutic Acceleration Program (Francis S. Collins Scholarship in Neurofibromatosis Clinical and Translational Research) at Johns Hopkins University. The contents of this abstract are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.References
1Raz et al, Mult Scler. 2015 Apr;21(5):562-71.
2Garaci et al, Neuroradiology. 2013 Feb; 55(2): 233–243.
3Xie et al, Am J Ophthalmol. 2007 Apr;143(4):642-6.
4Lennartsson et al, Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014 Nov 6;55(12):8278-88.
5de Blank et al, Neuro Oncol. 2013 Aug; 15(8): 1088–1095.
6de Blank et al, ISMRM 2016, abstract 3058.
Figures