2132
Sub-millimeter bSSFP isotropic T2 weighted breast imaging - results of a prospective clinical study to determine if specificity of breast MRI can be improved.1Radiology, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, United States, 2Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin, WI, United States
Synopsis
Although DCE-MRI is the mainstay of breast MRI diagnosis, specificity is limited due to multiple enhancing benign lesions. Specificity can by improved by viewing T2 information, but conventional T2 imaging is limited by spatial resolution. We performed a prospective clinical study of a novel T2-like imaging sequence with sub-mm spatial resolution to determine if a breast radiologist could improve his assessment of benignity. Results show that excellent spatial resolution was achieved, but at the cost of increased noise and loss of T2 contrast. Ultimately, the radiologist felt less confident in more cases than he felt more confident regarding benign lesions.
Purpose
Although DCE-MRI is the mainstay of breast MRI diagnosis, specificity can be compromised by multiple benign enhancing lesions. T2 relaxation characteristics can improve diagnostic accuracy1. For example, some fibroadenomas have high T2 signal intensity (SI) with thin internal septations, while lymph nodes have high T2 SI, a distinctive morphology and eccentric fatty hilus. In routine breast imaging, limited T2 spatial resolution diminishes the ability of MRI to make these subtle distinctions. High resolution bSSFP imaging provides large signal levels with short TRs of 3-6 ms, an approach roughly five times as efficient as a 3d RARE-based methods like FSE Cube. One downside is that bSSFP produces a T2-like contrast instead of pure T2 contrast. We performed a prospective clinical study to determine the ability of a novel T2-like imaging sequence with sub-millimeter isotropic spatial resolution to improve accuracy of breast MRI diagnosis
Methods
With IRB approval, patients were recruited from those coming for clinical breast MRI. Since most patients in our practice are referred for high risk screening and result in negative examinations, we enriched our population by recruiting patients with known cancers or suspected or known benign findings. The novel T2-like imaging sequence consisted of a 5 minute, unilateral 3D-radial balanced SSFP (bSSFP) sequence with 0.6mm isotropic resolution2 with fat suppression provided by a weighted combination SSFP reconstruction method2,3. Imaging was performed at 1.5T using a commercially available 8 channel breast array coil. Since the bSSFP sequence is affected by T1 shortening from Gd contrast, it was inserted into the clinical MRI protocol before contrast administration. In total 27 patients with 5 malignancies and 22 benign findings were imaged. For technical issues in 4 benign cases, and one malignant case, 5 patients were excluded from analysis. Images, blinded to diagnosis, were presented to a breast radiologist, with over 20 years experience, and read in three sessions with a 6 - 8 week washout period as follows: Panel A: clinical T2, early and late DCE-MRI, Panel B: bSSFP images substituted for clinical T2 imaging (reconstructed in same plane), no change in DCE-MRI images, and Panel C: imaging from Panel B + 2 orthogonal bSSFP imaging planes to fully exploit isotropic resolution, and 1 fat image. The radiologist was asked to provide a BI-RADS score as well as a numerical percent chance of benignity (PCB). Only PCB changes > 10% or single digit BI-RADS changes were considered significant. Diagnosis for the index MRI was established by biopsy or by at least 1 year of stability on prior or subsequent breast MRI.Results
Malignant Lesions: In 3/4 lesions, PCB was 10% (BI-RADS 4) and results were unchanged on Panels B and C. In 1/4 lesions, Panel A, PCB was 50% (BI-RADS 4), which stayed at 50% (BI-RADS 4) on Panel B, but on Panel C PCB was 30% (BI-RADS 4).
Benign Lesions: bSSFP imaging increased PCB in 1/18 patients. For this one patient, BI-RADS was changed from 3 to 2. bSSFP resulted in no significant change in PCB and/or BI-RADS in 12/18 patients. bSSFP imaging decreased PCB and/or BI-RADS in 5/18 patients
Discussion
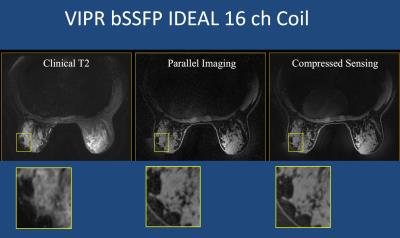
The goal of bSSFP imaging was to improve confidence in diagnosis of benign lesions through an eleven fold decrease in voxel size while still providing T2-like contrast. However, this was not borne out in practice as the radiologist lost confidence more frequently than he gained confidence when bSSFP was substituted for conventional T2 imaging. Increased noise due to radial undersampling artifact as well as decreased T2 SI hampered the radiologist’s ability to detect features of benignity. In future implementations, some of the SNR lost to higher resolution can be retrospectively returned by slice averaging the isotropic data in any direction during image review, or increasing the number of receiver coils, allowing the 3D radial sequence to take greater advantage of the PILS effect4. We have just acquired a 16 channel coil and will be implementing these changes. One unexpected finding was increased confidence in malignancy in one case where Panel C images improved perception of the irregular border.Conclusion
Isotropic high spatial resolution T2-like imaging made possible by the bSSFP sequence was expected to improve confidence in diagnosis of benign lesions, but this was not the case in this clinical trial. Increased noise due to undersampling and decreased T2 SI often hindered firm diagnosis of indeterminate enhancing lesions. The advent of 16 channel coils may provide clinically relevant improvements in image quality through reduction of the noise-like aliasing due to undersampling. Restoration of the desired T2 SI remains the subject of future research.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Kuhl CK, Klaschik S, Mielcarek P, et. al. Do T2-weighted pulse sequences help with differential diagnosis of enhancing lesions in breast MRI? J Magn Reson Imaging 1999;9(2):187-96.
2. Moran CJ, Kelcz F, Jung Y, Brodsky EK, et. al. Pilot study of improved lesion characterization in breast MRI using 3D radial balanced SSFP technique with isotropic resolution and efficient fat-water separation. J Magn Reson Imaging 2009;30(1):135-44.
3. Cukur T, Bangerter NK, Nishimura DG. Enhanced spectral shaping in steady-state free precession imaging. Magn Reson Med 2007;58(6):1216-23.
4. Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Nittka, et. al. Partially parallel imaging with localized sensitivities (PILS). Magn Reson Med 2000;44(4):602-9.
Figures
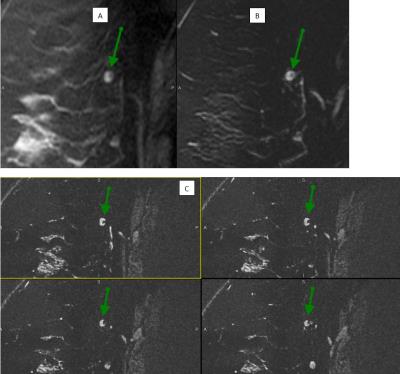
Figure 1: Normal axillary lymph node (green arrow)
(A) DCE-MRI shows enhancing lymph node with eccentric fatty hilum.
(B) Conventional T2-w imaging shows very high SI lymph node with vague fatty hilum on single slice.
(C) bSSFP T2-like group of four adjacent slices highlights superb sub-mm spatial resolution. Unlike (A) and (B), several images encompass, and display, to much greater advantage, the fatty hilum. Although T2 SI remains high, this is not the case for many lesions (see other included figures)
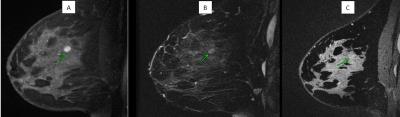
Figure 2: Stable lesion for 18 months, presumed fibroadenoma (green arrow).
(A) DCE-MRI shows oval circumscribed lesion with nonenhancing internal septations
(B) Conventional T2-w images shows low, but perceptible T2 contrast compared to surrounding normal tissue.
(C) bSSFP images shows virtually no contrast between lesion and parenchyma.
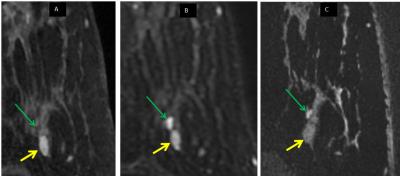
Figure 3: Small cluster of cysts (green arrow) adjacent to presumed fibroadenoma (yellow arrow, stable 26 months)
(A) DCE-MRI shows adjacent tiny, barely discernible areas representing non-enhancing fluid within poorly resolved cysts. These are adjacent to a homogeneously enhancing well marginated oval mass (presumed fibroadenoma).
(B) Conventional T2 image shows high T2 SI typical of tiny, unresolved cysts and high SI associated with some fibroadenomas.
(C) bSSFP now resolves three adjacent tiny cysts with high T2 SI, but presumed fibroadenoma has lost SI compared to b, now being isointense to fibroglandular tissue.