2127
The Significance of Joint Clinical Application of Digital Mammary Gland 3D Tomosynthesis with Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Diagnosis of Breast CancerWenwen Fan1, Han Ouyang1, Chunwu Zhou1, Xinming Zhao1, and Lizhi Xie2
1National Cancer Center/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, People's Republic of China, 2GE HealthCare, MR Research China, Beijing, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
Synopsis In recent years, the incidence rate of breast cancer in China has been rising rapidly, which highlights the importance of early diagnosis. Therefore, how to improve the detection rate and reduce the recall rate become significant for the breast cancer prevention and treatment. Considering the tissue overlapping effect from conventional digital mammary gland photography technology may lead to false positive and negative results.
Purpose
To acknowledge the significance of Joint Clinical Application of Digital Mammary Gland 3D Tomosynthesis with MRI for Diagnosis of Breast Cancer, and study their efficient clinical usage.Methods
Randomly choose 271 female patients, study 542 sides of Digital Mammary Gland 3D Tomosynthesis and MR images, comparing the diagnosis and pathology from the 253 patients, then analyzing and comparing them with MRI results. Implementing digital mammography under standard mode of Hologic mammary gland machine, to get the corresponding 2D and 3D images. At the same time, all of them were examined on a 3.0T MR system (MR 3.0T Twinspeed signa hdxt, GE Healthcare, America) with multiple-b-value diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) scans. The following imaging parameters were used for FS AX T2 IDEAL sequence (FOV=33×33cm, slice thickness=5.0mm, Echo Train Length=19, bandwidth=62.5, matrix=320×224, TE=85ms, TR=5440ms). The following imaging parameters were used for STIR AX DWI sequence (FOV=40×40cm, slice thickness=8.0mm, TE=Minimum, TR=4000, Inv. Time=160, NEX=2.0, matrix=128×128). The following imaging parameters were used for AX VIBRANT+C sequence (FOV=30×30cm, slice thickness=2.0mm, flip angle=15, bandwidth=62.5, matrix=388×256). GE AW4.6 workstation was used to calculate the value of ADC, ADC standard, D, D*, f, and to generate time-signal intensity curve (TIC). All parameters between benign and malignant breast lesions were compared by Mann-Whitney U test. Finally, we promote an analysis of breast cancer focus based on 114 cases of female patients identified by histopathology. The diagnostic performance of different parameters was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic curve analysis.Results and Discussion
After analyzing and comparing Digital 3D Tomosynthesis (Fig.1, Fig.2), MRI diagnosis (Fig.3) with the pathology from 253 patients, among which 130 patients were diagnosed with breast cancer and their pathology indicate positive, 16 cases’ pathological indicate negative; 11 patients were diagnosed with non-breast cancer, and 96 cases’ pathology indicate negative. This study shows that a 92.2% sensitivity rate of Digital Mammary Gland 3D Tomosynthesis technology for diagnosis of breast cancer, 85.7% of specificity, 89.3% of the coincidence rate, positive predictive value is 89%, and negative predictive value is 89.7%; A 89.7% sensitivity rate of MRI technology for diagnosis of breast cancer, 84.2% of specificity, 87.6% of the coincidence rate, positive predictive value is 87.4%, and negative predictive value is 86.4%.(Table 1)Finally the joint clinical application of Digital Mammary Gland 3D Tomosynthesis with MRI could not only reduce the false positive and negative rate, but also improve the test sensitivity and specificity1,2.Conclusion
The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of Digital Mammary Gland 3D Tomosynthesis technology are superior to MRI. Breast MR Examination is the effective method of breast cancer,so joint clinical application of Digital Mammary Gland 3D Tomosynthesis Technology with MRI is more valuable and efficient for diagnosis of breast cancer.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Park A M,Franken EA, Garg M, et al. Breast tomosynthesis: Present considerations and Future applications[J],Riadiographics ,2007(27):231-240.2.Fischmann A, Siegmann KC, Wersebe A, et al. Comparison of full-filed digital mammography and full-screen mammography :image quality and lesion detection[J].Radiology ,2005,78(928):312-317.
Figures
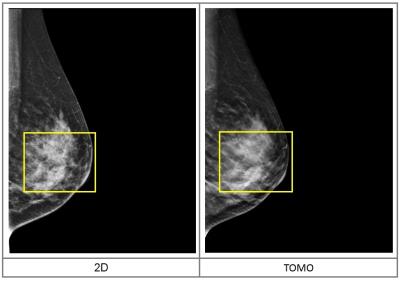
Figure.1 2D image and 3D Tomosynthesis Slices.

Figure.2 If we look on a single slice of the
3D tomosynthesis acquisition again,we can see the spiculated margins of this
mass.
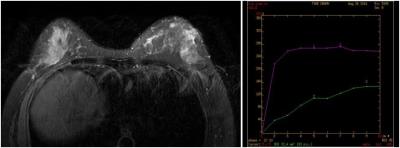
Figure.3 The left breast quadrant revealed a
lobulated nodule, Edge visible burr, Size of about 1.1cmx0.8cmx1.6cm, T2WI/FS
is signal, DWI diffusion limited, Enhanced scanning showed obvious enhancement,
Time signal curve is platform type.
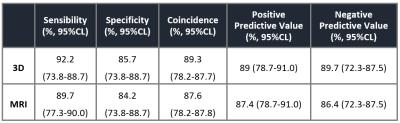
Table.1 The sensitivity of the 3D and the
coincidence rate is better than MRI, the difference was statistically
significant.