2122
Comparing the diagnosis efficiency of different parameters of diffusion kurtosis imaging model in benign and malignant breast lesions1The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, zheng zhou, People's Republic of China, 2GE Healthcare,MR Research China, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
In order to comparethe diagnosis efficiency of different parameters derived from diffusion kurtosis imaging model in benign and malignant breast lesions, eighty patients were analyzed in this study . DKI data with six b-values and 15 directions were acquired using single-shot SE-EPI sequence. The values of mean kurtosis (MK), axial kurtosis (AK) and radial kurtosis(RK) in malignant lesions group were significantly higher than those in benign lesions groups. The diagnosis efficiency of these parameters were also analyzed. The results showed that DKI-derived parameters can be used to distinguish the malignant lesions and benign lesions, especially AK and MK
PURPOSE:
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women in China, the incidence of which ranks first in all cancers of women [1]. As we all know, it is important to distinguish the benign and malignant lesions due to the different treatment and prognosis in varying degree lesions. However, these two breast lesions cannot always be discriminated accurately by using the conventional imaging technique, as diffusion weighted imaging (DWI),dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI),intravoxel incoherent motion imaging (IVIM), etc. As an advanced diffusion MR imaging techniques, diffusion kurtosis imaging(DKI) may reflect the microenvironment of breast tumor tissues[2]. DKI had been used in grading of gliomas[3], hepatic fibrosis [4] and hepatic carcinoma [5], but it is rarely used in breast. In previous studies, only mean kurtosis (MK) of DKI was used in the diagnosis of breast. In this study, DKI sequence with more directions was performed to obtain more parameters such as mean kurtosis (MK), axial kurtosis (AK) and radial kurtosis (RK). .And the diagnosis efficiency of different parameters derived from diffusion kurtosis imaging model were compared in benign and malignant breast lesions.METHODS:
A prospective study was reviewed by the ethics committee of the hospital. All recruited patients signed written informed consent. Ninety-six patients with breast lesions were recruited in this study, but sixteen patients were lost to follow up. Finally, eighty lesions in eighty patients (age range 17-65 years,42±1.4 years) were examined on 3.0T GE Discovery 750 with 8 channel bilateral breast coil. DKI data was acquired for 10 minutes 48 seconds using single-shot spin-echo pulse sequence (TR/TE-4015s/minimum, thickness 4mm, space 1mm, Matrix-256×256, FOV-32cm×32cm, six b-values 0,500,1000,1500,2000,2500s/mm2, 15 directions, NEX 2).Breast lesions were divided into two groups according to pathological characteristics. DKI-related parameters, MK, AK and RK, were measured after scanning. Acquired MR images were analyzed by two radiologists with over 5 years of experience in the diagnosis of breast lesions. Regions of interest (ROIs)significantly enhanced in the lesion were selected, except areas of cystic degeneration and necrosis. The parameters MK,AK and RK of malignant and benign lesions were compared by Mann-Whitney U tests. Receiver operation curve (ROC) analysis was performed to assess the sensitivity and specificity of MK,AK and RK in the diagnosis of breast lesions.RESULTS:
The values of MK,AK and RK in malignant lesions group were significantly higher than those in benign lesions groups (shown in Table 1).In addition, the current results showed that the sensitivity /specificity of these three parameters in the diagnosis of malignant were 77.8% /63.6%,75%/81.8%and 72.2%/63.6%.Respectively, the area under the curve of parameters MK, AK and RK were 0.728,0.782and 0.688 (shown in Figure 1).Figure 2and 3 showed the parameters images of two typical patients.DISCUSSION:
Diffusion kurtosis imaging model, as an extension of conventional DWI, was first described in Jensen’s paper [6], which can better reflect tissue complexity based on non-Gaussian PDF distribution assumption. It is known that the cellular microstructure of malignant lesions is more complex and heterogeneous than that of benign lesions. Therefore malignant lesions and benign lesions may be distinguished by some parameters derived from DKI. Parameter MK represented the averaged kurtosis in all directions, and parameters AK and RK represented kurtosis of the breast duct and gland in parallel and perpendicular directions. One possible explanation for highest specificity of AK is that pathologic changes along the direction of the pipe and gland my influence the water diffusion.CONCLUSIONS:
Our results showed that DKI-derived parameters could be used to distinguish the malignant lesions and benign lesions, especially AK and MK. Both of these two parameters had considerable sensitivity. Furthermore, AK had the highest specificity among all the diffusion kurtosis related parameters. This study demonstrates that AK and MK have the potential to be used as a biomarker in the diagnostic of breast lesions clinically.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Ma D, Lu F, Zou XIntravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging as an adjunct to dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI to improve accuracy of the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast lesions. Magn Reson Imaging.( 2016) Oct 11. Pii : S0730-725X(16)30152-7
2. Wu D, Li G, Zhang J. DKI has been used in cerebral glioma. PLoS One.(2014) Nov 18;9(11):e113240.
3. Van Cauter S, Veraart J, Sijbers J, Peeters RR, Himmelreich U, et al. Gliomas: Diffusion kurtosis MR imaging in grading. Radiology (2012)263 (2): 492–501
4. Anderson SW, Barry B, Soto J, Ozonoff A, O’Brien M, et al. Characterizing non-gaussian, high b-value diffusion in liver fibrosis: Stretched exponential and diffusion kurtosis modeling. J Magn Reson Imaging(2014) 39 (4): 827–34.
5. Rosenkrantz AB, Sigmund EE, Winnick A, Niver BE, Spieler B, et al. Assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma using apparent diffusion coefficient and diffusion kurtosis indices: perliminary experience in fresh liver explants. Magn Reson Imaging (2012) 30 (10): 1534–40
6. Jensen J, Helpern J, Ramani A, Lu H, Kaczynski K Diffusion kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med (2005)53:1432–1440
Figures
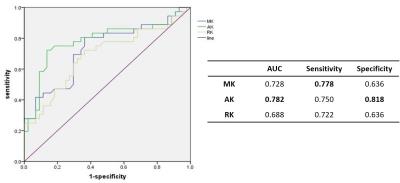
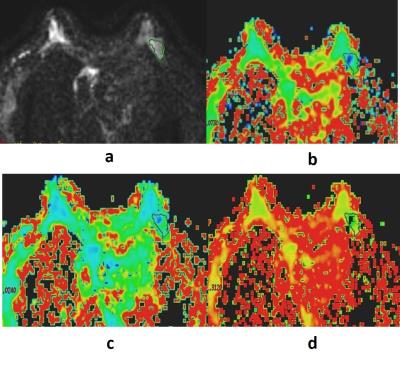
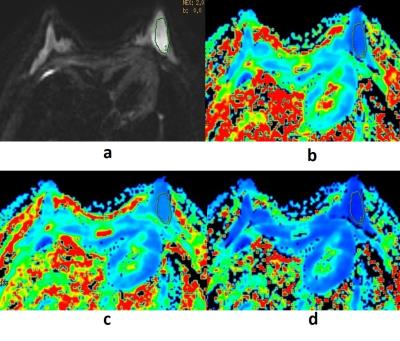
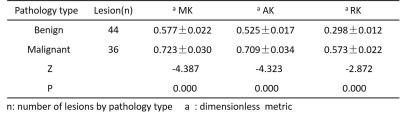
Table 1 Comparison different diffusion variables between the two pathology types