2103
Benign prostatic hyperplasia after prostatic arterial embolization in a canine model: a 3T multi-parametric MR imaging and whole-mount step-section pathology correlated longitudinal study1Department of Radiology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, People's Republic of China, 2Department of Radiology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology
Synopsis
Prostatic arterial embolization (PAE) is a minimally invasive procedure developed in the recent years. Recent studies reported clinical applications of PAE in the treatment of BPH, and its safety and efficacy was confirmed. For the basic theory research, some scholars have made preliminary animal experiments in beagle dogs and pigs.To the best of our knowledge, there is no longitudinal study regarding BPH morphological and functional characteristics of BPH in different periods after PAE with multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (mp-MRI).
Purpose
To explore the morphological and functional characteristics of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) 6 months after prostatic arterial embolization (PAE) in a canine model with 3T multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (mp-MRI) and whole-mount step-section pathology correlationMaterials and Methods:
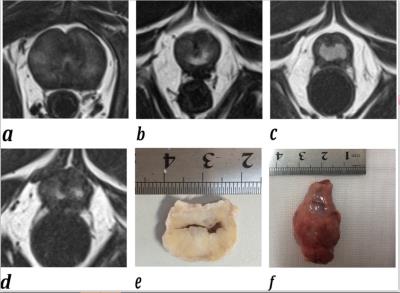
Eight adult male beagle dogs with hormone-induced BPH underwent mp-MRI before and 1, 3, and 6 months after PAE, with subsequent whole-mount step-section pathologic assessment after sacrifice. All the dogs were sacrificed for imaging and whole-mount step-section pathology correlation. Variance analysis was performed to assess statistical differences in prostatic volume (PV), apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value, and T2 relaxation time (T2RT) value. Pearson correlation analysis was performed to correlate ADC value, T2RT and PV, respectively. P<0.05 indicates a statistically significant difference.Results
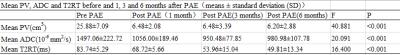
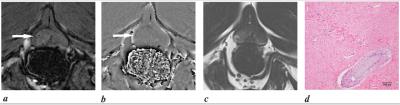
The PV value before and 1 month after PAE was 25.88 ± 7.09 cm3 and 6.48 ± 2.08 cm3 (P < 0.001). The ADC values before and 1, 3 and 6 months after PAE were (1497.06 ± 222.72) × 10-6 mm2/s, (1056.00 ± 189.46) × 10-6 mm2/s, (950.48 ± 77.85) × 10-6 mm2/s and (980.98 ± 107.78) × 10-6 mm2/s, respectively. The average of quantitative pharmacokinetics parameters of Ktans,Kep and Ve six months after PAE were (0.09 ± 0.08) /min,(0.45 ± 0.31) /min,(0.38 ± 0.12),respectively. The T2RT values before and 1, 3 and 6 months after PAE were (83.74 ± 5.29) ms, (68.72 ± 5.66) ms, (53.96 ± 15.04) ms, (49.81 ± 13.34) ms, respectively. ADC and T2RT values were positively correlated with PV (r=0.823 and 0.744, respectively). Micro-hemorrhages and hemosiderin were found in all beagle dogs on SWI 1, 3, and 6 months after PAE.Conclusion
3T mp-MRI may facilitate noninvasive assessment of longitudinal morphological and functional changes of BPH after PAE.Acknowledgements
Contract grant sponsor: National Natural Science Founda-tion of China; Contract grant number: 81171307References
1 Pisco JM, Rio Tinto H, Campos Pinheiro L, et al. Embolisation of prostatic arteries as treatment of moderate to severe lower urinary symptoms (LUTS) secondary to benign hyperplasia: results of short- and mid-term follow-up. Eur Radiol 2013;23(9):2561-2572.
2 Sun F, Sanchez FM, Crisostomo V, et al. Transarterial prostatic embolization: initial experience in a canine model. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2011;197(2):495-501
3 Jeon GS, Won JH, Lee BM, et al. The effect of transarterial prostate embolization in hormone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia in dogs: a pilot study. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2009;20(3):384-390
Figures