Li Ya-Hui1, Chen Ran-Chou, Huang Wen-Yen, Chang Wei-Chou, and Tang Zun-Cheng
1Tri-Service general hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
Synopsis
Functional imaging
techniques have a potential role in evaluation of treatment response in
patients with HCC after SABR. After SABR, the increase of ADC value > 10%
had marginally improved local control. A further large-scale study to identify
the predictive value of parameters in functional MRI in validated.
Purpose/Objective(s)
While stereotactic
ablative radiotherapy (SABR) has emerged as a treatment option for hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC), there are limited data on treatment response evaluation. Functional
imaging techniques are increasingly being used to monitor response to therapy. The
aim of this study was to evaluate response of the target tumor by functional
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including diffusion-weighted imaging and its
impact on local control in patients with HCC after SABR.Material/methods
Between Dec 2008 and Nov
2014, 31 HCC patients with 37 tumors underwent SABR using Cyberknife
radiosurgery system in our institute. The median radiation dose was 45 Gy
(range: 30-60 Gy), 6-12.5 Gy per fraction. We collected clinical and treatment-related
and factors including age, ECOG performance status, α-fetoprotein (AFP) level, Child-Pugh
score, CLIP score, and AJCC stage. All patients had pretreatment and 1- to 3-
month follow-up MRI. Response using volumetric functional apparent diffusion
coefficient (ADC) was assessed in all target tumors. Local control was defined
as the target tumors with no increase size of enhancing part on
contrast-enhanced images.
Results
At the last follow up, 16
patients died. The median survival was 13.7 months, with 1-year and 2-year OS
rate of 62.9% and 40.0%, respectively. There were 7.4% complete response, 70.4%
partial response, 14.8% stable disease, and 7.4% disease progression. There
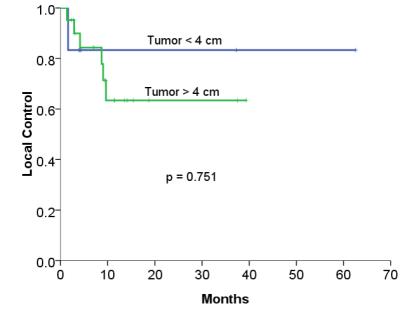
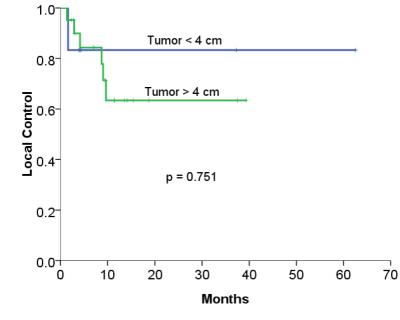
were 8 target tumors with local failure and 2-year local control rate was
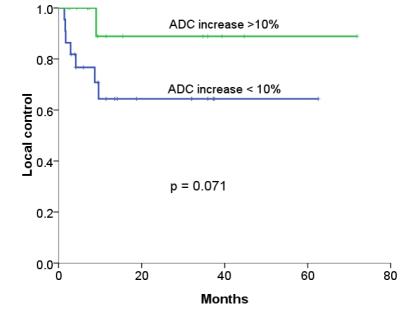
73.8%. There was a trend of better 2-year local control in tumors with
post-treatment ADC value increase > 10%, compared with those <10% (88.9%
vs 64.4%, p = 0.071).Conclusions
Functional imaging
techniques have a potential role in evaluation of treatment response in
patients with HCC after SABR. After SABR, the increase of ADC value > 10%
had marginally improved local control. A further large-scale study to identify
the predictive value of parameters in functional MRI in validated.Acknowledgements
We would like to give special thanks to Benjamin Yen, professor in University of California, San Francisco, for his guidance and helpReferences
No reference found.