2065
Histogram analysis of pharmacokinetic parameters of DCE-MRI: differentiating malignant from benign solitary pulmonary nodules1Nantong Tumor Hospital, Nantong, People's Republic of China, 2Nantong Tumor Hospital, 3Shanghai East Hospital
Synopsis
A histogram analysis approach has been shown to be a premising tool in discriminating malignant and benign SPNs in terms of their heterogeneity. The purpose of our study was thus to primarily assess the diagnostic performance of DCE-MRI for stratifying the malignant and benign using histogram analysis. The results showed that the mean value of Ktrans and Kep, Kurtosis and skewness assessments from Ve of DCE-MRI histograms may be useful for differentiating malignant from benign SPNs.
Introduction
Quantitative dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) reveals the tissue perfusion and permeability by its pharmacokinetics parameters and often applied for the cancer study in terms of differentiating malignant from benign tumors. Before, the mean value of each quantitative parameters was the only label which could not demonstrate the heterogeneity of the tumors. Histogram analysis is a useful tool of distinguishing the tumor’s heterogeneity.Before, for lung imaging, most studies focused on the density histogram analysis using CT which could provide meaningful information on the characteristics of lung nodules 1,2. Little study of histogram analysis of DCE-MRI for the differential diagnosis of solitary pulmonary nodules (SPNs) . Thus, our study aim was to prospectively evaluate histogram analysis of pharmacokinetic parameters of quantitative DCE-MRI for discriminating malignant and benign SPNs.
Methods
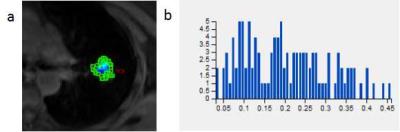
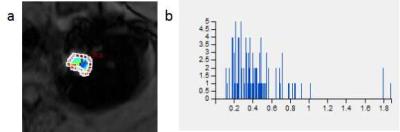
Institutional review board approval and written informed consent were obtained. 51 consecutive patients (31 males and 20 females;Age range from 35 to 78 years old and their mean value: 61 years) with SPNs were included in this prospective study. 33 SPNs were malignant, the other 18 were benign. All these patients underwent DCE-MRI. The quantitative MR pharmaeokinetic parameters including volume transfer constant (Ktrans), transfer constant from the extracellular extravascular space to plasma (Kep), extra-vascular extra-cellular space fractional volume (Ve) were calculated using Extended-Tofts Linear two compartment Model. Mean, Kurtosis and skewness of the three MR pharmacokinetic parameters from DCE-MRI were measured. These parameters were statistically compared the difference between the malignant and benign nodules using the Mann–Whitney U test. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses were used to calculate the diagnostic capability.Results
The mean value of Ktrans and Kep in the malignant lesions was significantly higher than those in the benign lesions (0.128±0.073 vs 0.069±0.036, and 0.580±0.244 vs 0.405±0.202, respectively, P=0.003 and 0.012). Kurtosis and skewness from Ve in the malignant lesions were significantly lower than those in the benign lesions (0.826±0.783 vs 3.285±2.341 and 1.228±1.171 vs 5.057±3.291, respectively, P<0.001). The areas under the ROC curve (AUC) of the mean value of Ktrans and Kep, Kurtosis and skewness from Ve between malignant and benign nodules were 0.791, 0.715, 0.815, 0.882, respectively. The sensitivity of the mean value of Ktrans and Kep, Kurtosis and skewness from Ve were 84.8%, 75.8%, 77.8%and 88.9% and specificity were 72.2%, 72.2%, 81.8%, 72.7% for the differential diagnosis of SPNs.Discussion
The malignant SPN tissue has higher microvascular density and tumor angiogenesis and results in much more permeable capillaries 3. More and more contrast media accumulate in extra-vascular extra-cellular space, that’s why Ktrans and Kep are markedly increased in malignant nodules compared with benign nodules 4,5. In fact, in malignant tissue the microstructural environment with dense tumor cell membranes, larger cell nuclei and higher cellular density is known to act as a diffusion barrier 6,7. A decrease of the kurtosis and skewness from Ve has been demonstrated to be indicative for various malignancies. The different kurtosis and skewness from Ve may reveal the inhomogeneity of the extra-cellular space tissue density.Conclusion
The mean value of Ktrans and Kep, Kurtosis and skewness assessments from Ve of DCE-MRI histograms may be useful for differentiating malignant from benign SPNs.Acknowledgements
NoReferences
1. Yamashiro T, Matsuoka S, Estepar R S, et al. Kurtosis and skewness of density histograms on inspiratory and expiratory CT scans in smokers. COPD,2011,8(1):13-20.
2. Matsuoka S, Kurihara Y, Yagihashi K, et al. Quantification of thin-section CT lung attenuation in acute pulmonary embolism: correlations with arterial blood gas levels and CT angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol,2006,186(5):1272-1279.
3. Ohno Y, Nishio M, Koyama H, et al. Solitary pulmonary nodules: Comparison of dynamic first-pass contrast-enhanced perfusion area-detector CT, dynamic first-pass contrast-enhanced MR imaging, and FDG PET/CT. Radiology. 2015,274(2):563-575.
4. Mamata H, Tokuda J, Gill R R, et al. Clinical application of pharmacokinetic analysis as a biomarker of solitary pulmonary nodules: dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Magn Reson Med. 2012,68(5):1614-1622.
5. de Langen A J, van den Boogaart V, Lubberink M, et al. Monitoring response to antiangiogenic therapy in non-small cell lung cancer using imaging markers derived from PET and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI. J Nucl Med. 2011,52(1):48-55.6. Sun K, Chen X, Chai W, et al. Breast Cancer: Diffusion Kurtosis MR Imaging-Diagnostic Accuracy and Correlation with Clinical-Pathologic Factors. Radiology,2015,277(1):46-55.
7. Kamiya A, Murayama S, Kamiya H, et al. Kurtosis and skewness assessments of solid lung nodule density histograms: differentiating malignant from benign nodules on CT. Jpn J Radiol,2014,32(1):14-21.
Figures