2022
Evaluation of Intravoxel Incoherent Motion with Different b Values in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma1Department of Radiology, Shanghai Institute of Medical Imaging, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, People's Republic of China, 2Department of Radiology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, 3Siemens Healthcare, Shanghai, P.R. China
Synopsis
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) model provides both pure water motion and microcirculation by using multiple b values. IVIM imaging has been shown to be useful for assessment of liver diseases, including liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. However, the clinical implementation of IVIM imaging is limited by long acquisition time. We compared IVIM imaging with different b-values to determine the combination of b-values in IVIM imaging that allows the relatively short acquisition time to obtain reproducible values of the IVIM parameters in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Our results showed at least 10b-values should be used in IVIM imaging for the assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma, and 5b-values IVIM imaging might increase errors in the perfusion-related f and D* values.
INTRODUCTION
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) model provides both pure water motion and microcirculation by using multiple b values. IVIM imaging has been shown to be useful for assessment of liver diseases, including liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma1,2. However, the clinical implementation of IVIM imaging is limited by long acquisition time. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to determine the combination of b-values in IVIM imaging that allows the relatively short acquisition time to obtain reproducible values of the IVIM parameters in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.METHODS:
Free-breath IVIM imaging with 13 b values (Protocol A) and 5 b values (Protocol B) were performed at 1.5 T MR scanner (MAGNETOM Aera, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) in 10 patients (2 females, 8 males; mean age 52) with 11 hepatocellular carcinomas. The IVIM imaging parameters of both protocols were as follows: echo time=4500ms, repetition time=51ms, acquisition matrix=128×128, slices=25, slice thickness=5mm. For Protocol A, b values at 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100,150, 200, 400, 780, 800 s/mm2 were selected, numbers of averages were 0 (b=0 s/mm2), 2 (b≤200 s/mm2) or 4 (b>200 s/mm2), and acquisition time was 7min4s; For Protocol B, b values at 0, 15, 40, 150, 800 s/mm2 were selected, number of averages was 6, and acquisition time was 6min1s. IVIM parameter maps, including the diffusion coefficient D, the pseudodiffusion coefficient D* and the perfusion fraction f, and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) were generated by using a prototype software body diffusion toolbox (Siemens Healthcare, Germany), and the protocol A was then split into two 10 b-values protocols: 0, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 150, 200, 400, 800 s/mm2 (Protocol C) and 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 150, 200, 780, 800 s/mm2 (Protocol D) to acquire the corresponding parametric maps in the same software. A single representative region of interest was traced manually along the margin of the tumor at the slice containing the largest tumor, excluding areas of hemorrhage and necrosis. Intrarobserver agreement of the IVIM model parameters was evaluated by using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC), and the differences between these four protocols were assessed by using two-way analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test.RESULTS
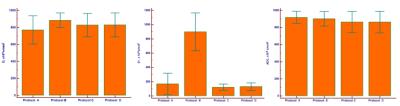
Representative images of D, D*, f and ADC are provided in Figure 1. Intrarobserver measurements revealed good agreement (ICC=0.81~0.93). The distribution of IVIM parameters (D and D*) and ADC for the tumor of different combination of b values are provided in Figure 2, revealing D values (P=0.351) and ADC (P=0.244) were not significantly different between the different protocols, but D* values (P<0.001) and f values (P <0.001) were different between Protocol B and other protocols.DISCUSSION
Although IVIM becomes more and more popular, there is currently no clear consensus on the number and distribution of b-values to use3. With more b values being applied, IVIM imaging may not well tolerated by patients due to long scan time. We acquired IVIM imaging with different b values, the results showed that 5b-values might increase errors in the perfusion-related f and D* values because of limited number of low b values.CONCLUSION
At least 10b-values should be used in IVIM imaging for the assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma, and 5b-values IVIM imaging might increase errors in the perfusion-related f and D* values.Acknowledgements
No.References
1.Wu C H, Ho M C, Jeng Y M, et al. Assessing hepatic fibrosis: comparing the intravoxel incoherent motion in MRI with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging in US[J]. European radiology, 2015, 25(12): 3552-3559.
2.Woo S, Lee J M, Yoon J H, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation with enhancement degree and histologic grade[J]. Radiology, 2013, 270(3): 758-767.
3.Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Protocol Evaluation and Data Quality in Normal and Malignant Liver Tissue and Comparison to the Literature
Figures