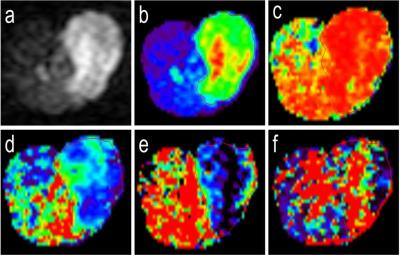
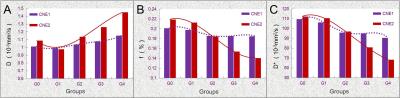
1831
IVIM-derived parameters in evaluating the pathological features and hypoxia of nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts1Radiology, Fujian Medical University Cancer Hospital, Fuzhou, People's Republic of China, 2Radiation Oncology, Fujian Medical University Cancer Hospital, Fuzhou, People's Republic of China, 3Philips Healthcare, Shanghai, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion weighted imaging was conducted on different radio-sensitive human NPC xenografts (CNE-1 and CNE-2) in order to investigate its application value in assessing the pathological features and tumor’s hypoxia of xenografts. CNE-2 xenografts of higher radio-sensitivity behaved greater changes on IVIM-parameters than CNE-1 xenografts of lower radio-sensitivity after fractional radiations. D and f values correlated significantly with the pathological features and tumor’s hypoxia of xenografts. Thus, IVIM-parameters is potentially valuable in evaluating the effect of radiotherapy in NPC.
Purpose
To preliminary investigate the value of intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) parameters in evaluating the pathological features and tumor’s hypoxia of different radio-sensitive nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) xenografts.Materials and methods
Two different radio-sensitive human NPC cell lines (CNE-1 and CNE-2) were transplanted on sixty nude mice (30 in each group) to raise xenografts, which received the fractional radiations (fraction of 10Gy at alternative days). Each group was then randomly subcategorized into five groups as following: non-radiation(G0), and radiation of 10Gy(G1), 20Gy(G2), 30Gy(G3), and 3-days after 30Gy(G4). On a 3.0T MR system, IVIM scans using 14 b-factors (0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 100, 150, 200, 350, 500, 600, 800, 1000 s/mm2) was performed on G0 directly without any radiation, G1~G3 after relative radiations completed and G4 at the third day after whole dose of radiation accordingly. IVIM-parameters of xenografts were analyzed and calculated with the IDL6.3 software. The cell density, necrosis proportion and HIF-1α expression of xenografts were analyzed histopathologically. Then, IVIM-parameters and pathological features were compared by Student t test and/or Mann-Whitney U test, and correlations between different variables were analyzed with Spearman test on the SPSS 18.0.Results
After fractional radiations, a larger D value, necrosis proportion and HIF-1α expression as well as a smaller D* value, f value and cell density were observed on NPC xenografts. CNE-2 xenografts presented significantly greater changes on the IVIM-parameters, necrosis proportion and cell density than those of CNE-1 xenografts during the course of fractional radiations (all P<0.01), while CNE-1 xenografts owned a significantly larger change on the HIF-1α expression than CNE-2 xenografts (P<0.005). Furthermore, D value correlated negatively with the cell density (rs=-0.861, P<0.001) and HIF-1α expression (rs=-0.814, P<0.001) but positively with the necrosis proportion (rs=0.952, P<0.001). Whereas, f value behaved a positive correlation with the cell density (rs=0.627, P<0.001) and a negative correlation with the necrosis proportion (rs=-0.649, P<0.001).Conclusion
Higher radio-sensitive CNE-2 xenografts behaved greater changes on IVIM-parameters after fractional radiations, which also correlated significantly with the pathological features and tumor’s hypoxia of human NPC xenografts.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Hong J, Yao Y, Zhang Y, et al. Value of magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging for the prediction of radiosensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013;149(5):707-13.
2. Bisdas S, Braun C, Skardelly M, et al. Correlative assessment of tumor microcirculation using contrast-enhanced perfusion MRI and intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI: is there a link between them?[J] NMR Biomed. 2014; 27(10):1184-91.
3. Koh DM. Science to practice: can intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging be used to assess tumor response to antivascular drugs?[J] Radiology. 2014; 272(2):307-8.
4. Pan J, Zang L, Zhang Y, et al. Early changes in apparent diffusion coefficients predict radiosensitivity of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts[J]. Laryngoscope. 2012;122(4):839-43.