1828
Prediction of Radiotherapy Response in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients Using Diffusion-Kurtosis Imaging1Department of Radiology, Hainan General Hospital, Haikou, People's Republic of China, 2Department of Radiology, Hainan General Hospital, People's Republic of China, 3Department of Radiology, Hainan General Hospital, Haikou, China, People's Republic of China, 4department of Radiology, Hainan General Hospital, People's Republic of China, 5MR scientific marketing NE Asia, Siemens Healthcare
Synopsis
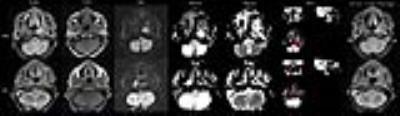
The first row: A 62-year-old man with NPC who was a nonresponder. The lesions located at the left nasopharyngeal wall and cavum. Manual draw an ROI within the boundaries of the NPC on Kmean map. The tumor’s maximum diameter was 3.5 before radiotherapy. Residual tumor was detected after radiotherapy. Mean Dmean and Kmean values were 1.48 10-3 mm2/s and 0.72 before treatment. The second row: A 63–year-old man with NPC who was a responder. The lesion affect the bilateral mucous membrane of the nasopharynx. The tumor’s maximum diameter was 3.09 before radiotherapy. No residual tumor was detected after radiotherapy. Mean Dmean and Kmean values were 1.22 10-3 mm2/s and 0.83 before treatment. NRG: non response group RG: reponse group
Introduction
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is one of the most common malignancies in Southeast Asia[1].
Early prediction of radiotherapy response to NPC may help clinicians to carry
out individual treatment and
avoid unnecessary systemic toxicity[2]. A
number of studies have shown the possibility of diffusion weighted imaging (DWI)-MRI to
prospectively predict the treatment response in different tumors[3-6]. The premise of monoexponential DWI is that water
diffusion in vivo obeys standard Gaussian distribution[7]. However, water diffusion in vivo is much more complex
than standard Gaussian distribution due to diffusion barriers like cell
membranes. Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) is an emerging new technique, based on a non-Gaussian diffusion model
that should better account for restricted water diffusion within the complex
microstructure of most tissues[8]. This study aimed to explore the clinical application of
DKI in the early prediction of the response to radiotherapy of NPC.Methods
Twenty-six patients with NPC were consecutively recruited in this prospective study. All the TNM statuses were determined according to the latest 7th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system[9]. All patients were imaged by using a 3T MR scanner (MAGNETOM Skyra, Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with 8-channel head and neck array coil pretreatment and 3th months after radiotherapy. MR imaging examinations included T1-weighted imaging, proton density-weighted imaging, DWI and DKI sequences. A fat-suppressed single-shot spin echo EPI sequence was used in the axial plane, TR/TE=8300/72 msec, Slice thickness=4 mm, FOV=230*240 mm, scan time =10:57 min, using thirty orthogonal diffusion directions for DKI examination with b values (0, 500, 1000, 1500 sec/mm2). DKI parameters (including fractional anisotropy (FA), apparent diffusion coefficient (D), and principle kurtosis eigenvectors (K)) were measured pretreatment using in-house software based on the formula: Sb/S0=exp[-b*ADC0+K*(bADC0)2/6]. Three months after the end of radiotherapy, patients were classified as response group and non-response group according to the assessment of short-time radiotherapeutic effect by Word Health Organization's response evaluation criteria. Mann-Whitney U-test was used to compare DKI parameters between groups. The performance of DKI parameters in prediction of radiotherapy responses was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic curve analyses and binary logistic regression.Results
Three months after radiotherapy, residual local tumors were detected in 7 (30.4%) cases, and no residual tumors in 16 (69.6%) cases. The maximum diameter of tumors in response group was lower than non-response group before radiotherapy, but there was no statistically difference (p=0.103). All DKI parameters were statistically different between groups (p<.05), and the differences in Kax, Kmean, Krad, and FA were statistically significant (p<.01). Krad at 0.76 was the best parameter to predict radiotherapy response with 71.4% sensitivity, 93.7% specificity (AUC:0.897, 95% CI, 0.756-1). Binary logistic regression showed age, T staging and DKI parameters were considered as the independent factors for response to radiotherapy.Discussion and Conclusion
The K(Kax, Kfa, Kmean and Krad) parameters represent the excess diffusion kurtosis in the tissue and are believed to be associated with microstructural complexity in vivo. Our result documented pretreatment values of DKI were found to correlate significantly with later tumor response/nonresponse. This correlation implies that NPC lesions with high pretreatment diffusivity (Dax, Dmean and Drad) values and low pretreatment kurtosis (Kax, Kfa, Kmean and Krad) values, indicating high viability and low heterogeneity, will respond better to radiotherapy. Our results demonstrate the feasibility of using DKI for pretreatment prediction of response to therapy in patients with NPCs undergoing radiotherapy.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1 Jiang H, Wang G, Song H, et al. Analysis of the efficacy of intensity-modulated radiotherapy and two-dimensional conventional radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma with involvement of the cervical spine. Oncol Lett. 2015 Nov; 10(5): 2731-2738.
2 Li S, Liu T, Mo W, et al. Prognostic value of phosphorylated Raf kinase inhibitory protein at serine 153 and its predictive effect on the clinical response to radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiat Oncol. 2016 Sep 20; 11(1): 121. doi: 10.1186/s13014-016-0696-5.
3 Huang WY, Wen JB, Wu G, Yin B, Li JJ, Geng DY. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for Predicting and Monitoring Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma Treatment Response. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016 Jul 7. [Epub ahead of print]
4 Foti PV, Longo A, Reibaldi M, et al. Uveal melanoma: quantitative evaluation of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the response assessment after proton-beam therapy, long-term follow-up. Cancer Imaging. 2016 Aug 19; 16(1): 23. doi: 10.1186/s40644-016-0080-6.
5 King AD, Thoeny HC. Functional MRI for the prediction of treatment response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: potential and limitations. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016 Oct 26. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25527. [Epub ahead of print]
6 Chen X, Ma Z, Huang Y, et al. Multiparametric MR diffusion-weighted imaging for monitoring the ultra-early treatment effect of sorafenib in human hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016 Oct 26. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25527. [Epub ahead of print]
7 Liu K, Ouyang H, Zhou CW, Tao H. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. Preliminary application of diffusion-weighted imaging with 3.0 T magnetic resonance scanner for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. 2010 Apr; 32(2): 200-4. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2010.02.015. Chinese.
8 Hori M, Fukunaga I, Masutani Y, et al. Visualizing non-Gaussian diffusion: clinical application of q-space imaging and diffusional kurtosis imaging of the brain and spine. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2012; 11(4): 221-33. Review.
9 Jiang R, Jiang J, Zhao L, et al. Diffusion kurtosis imaging can efficiently assess the glioma grade and cellular proliferation. Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 8; 6(39): 42380-93. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.5675.
10 Kamagata K, Tomiyama H, Hatano T, et al. A preliminary diffusional kurtosis imaging study of Parkinson disease: comparison with conventional diffusion tensor imaging. Neuroradiology. 2014 Mar; 56(3): 251-8. doi: 10.1007/s00234-014-1327-1.
11 Gao Y, Zhang Y, Wong CS, et al. Diffusion abnormalities in temporal lobes of children with temporal lobe epilepsy: a preliminary diffusional kurtosis imaging study and comparison with diffusion tensor imaging. NMR Biomed. 2012 Dec; 25(12): 1369-77. doi: 10.1002/nbm.2809.
12 Chen Y, Ren W, Zheng D, et al. Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Predicts Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Responses Within 4 Days in Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015 Nov;42(5):1354-61. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24910.
13 Zong J, Lin S, Lin J, et al. Impact of intensity-modulated radiotherapy on nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Validation of the 7th edition AJCC staging system. Oral Oncol. 2015 Mar; 51(3): 254-9. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2014.10.012.
14 Chen Y, Ren W, Zheng D, et al. Feasibility of diffusional kurtosis tensor imaging in prostate MRI for the assessment of prostate cancer: Preliminary results. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015 Nov; 42(5): 1354-61. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24910.
15 Chen Y, Liu X, Zheng D, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for early response assessment of chemoradiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Magn Reson Imaging. 2014 Jul; 32(6): 630-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2014.02.009.
16 Hong J, Yao Y, Zhang Y, et al. Value of Magnetic Resonance Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for the Prediction of Radiosensitivity in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013 Nov; 149(5): 707-13. doi: 10.1177/0194599813496537.
17 Jing Yuan, David Ka Wai Yeung, Greta S. P. Mok, et al. Non-Gaussian Analysis of Diffusion Weighted Imaging in Head and Neck at 3T: A Pilot Study in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. PLoS One. 2014 Jan 23; 9(1): e87024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087024. 17 Wu D, Li G, Zhang J,et al. Characterization of Breast Tumors Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging (DKI). PLoS One. 2014 Nov 18; 9(11): e113240. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113240.$$
Figures