1823
A Comparison of Readout Segmented EPI and Interleaved EPI in High Resolution Diffusion Weighted Imaging1Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, Beijing, People's Republic of China, 2BIU Clinical Science MR, Philips Korea, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 3Healthcare Department, Philips Research China, Shanghai, People's Republic of China, 4Vascular Imaging Laboratory, Department of Radiology, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States
Synopsis
Multi-shot interleaved EPI (iEPI) and readout segmented EPI (RS-EPI) are two alternative strategies for high resolution diffusion imaging. This study made a comparison of the two methods in different aspects. Our comparison showed that the iEPI had the advantage of largely reducing the geometric distortion. Both RS-EPI and iEPI could achieve high resolution diffusion tensor imaging.
Purpose
Single shot EPI has been widely used for diffusion weighted imaging in clinical applications due to its short scan time and insensitivity to motion. To improve the spatial resolution and reduce the susceptibility artifacts, multi-shot EPI methods have been proposed(1-3), which mainly fall into two categories, i.e. readout segmented EPI (RS-EPI)(4, 5) and interleaved EPI(iEPI)(2, 6, 7). To our best knowledge, both methods are well developed and can achieve higher resolution and reduced distortion than single shot EPI, but there are still no data comparing these two techniques explicitly. In this study, we aim to make a comparison between these methods. Our comparison focuses on the geometric distortion level and the performance in DTI.Methods
Both iEPI and RS-EPI sequences with a 2D navigator (4-7) were implemented on a Philips 3T Achieva TX scanner. In vivo brain diffusion imaging data were acquired using an eight-channel head coil. To minimize the data corruption caused by cardiac motion, cardiac triggering using PPU with a 100ms delay was used for all diffusion sequences. The gradient mode with magnitude of 40mT/m and slew rate of 200mT/m/ms was used for all sequences.
Geometric Distortion
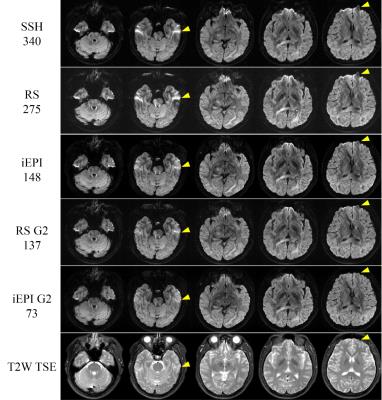
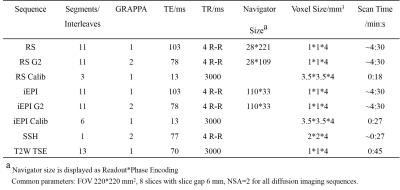
The echo time (TE) was set to the shortest for RS-EPI and the same TE was used for iEPI. The readout bandwidth was set to 312.5 KHz for both sequences. Each RS-EPI or iEPI sequence was acquired twice, one using full sampling and the other using GRAPPA=2. Note that for RS-EPI, the 2D navigator had the same size as the image echo, while for iEPI the 2D navigator used a fixed number of phase encoding lines (33 here). Both methods used the same acceleration factors for the image echo and navigator. Diffusion images were acquired at b=1000 s/mm2 in three orthogonal directions. Two low resolution EPI sequences used as the calibration data were acquired, with the effective echo spacing close to the corresponding sequence being calibrated. One single shot EPI diffusion imaging sequence was also acquired for comparison. T2 weighted TSE images were acquired as an anatomical reference. Detailed scan parameters are shown in Table 1.
DTI
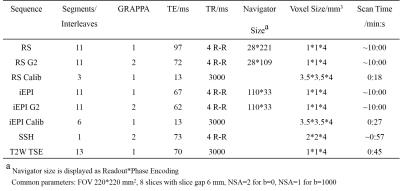
Each RS-EPI or iEPI sequence was acquired twice, same as experiment 1, except that the shortest TE was used for both sequences. Diffusion images were acquired at b=1000 s/mm2 in 16 directions. Other sequences and scan parameters are shown in Table 2.
Image Reconstruction
iEPI images were reconstructed using a k-space method described in (7). RS-EPI images were reconstructed using the algorithm described in (4). All procedures were implemented using Matlab.
Image Processing
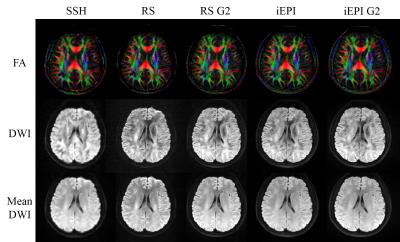
Motion correction and eddy current correction were performed on the data in experiment 2 using eddy_correct in FSL. FA maps were then calculated using DTIStudio.
Results
Geometric Distortion
The geometric distortion of the images decreased as the effective echo spacing decreased(Figure 1). Both RS-EPI and iEPI can achieve higher resolution and lower distortion than single-shot EPI. Given the same number of shots and acceleration factor, the iEPI images showed lower distortion than the RS-EPI.
DTI
Both RS-EPI and iEPI had higher resolution and revealed finer structures than single shot EPI, as shown in the color coded FA maps in Figure 2.
Discussion
In this study, iEPI is shown to be more capable of reducing distortion than RS-EPI. This is because the effective echo spacing of iEPI is inversely proportional to the number of interleaves, given the same FOV and target resolution. However, RS-EPI acquires the data mostly during the ramping up and down of the gradients due to a short traversal in the readout direction, resulting in longer TE and longer echo spacing than iEPI. For RS-EPI, the use of GRAPPA acceleration can largely reduce the TE and geometric distortion, while for iEPI, TE and distortion can be further reduced using more shots and/or parallel imaging acceleration. In this study, both methods relied on a 2D navigator for the phase correction. RS-EPI had the feature that the bandwidth of the image echo and the navigator echo were exactly the same, which was not the case for current iEPI. The navigator mismatch for iEPI might cause SNR loss and image artifacts(8). Currently we use cardiac triggering to avoid severe data corruption. This leads to variable TR and low scan efficiency. A further comparison should be made in a more practical situation such as using online reacquisition(4).Conclusion
For high-resolution multi-shot EPI diffusion imaging, the iEPI has the advantage of largely reducing the geometric distortion. Both RS-EPI and iEPI can achieve high resolution DTI.Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Philips MR Paradise Community for all the tips and clues on our sequence programming especially the kind help of Dave Higgins, Matthew Clemence, Ryan Robison and Zhongxu An.References
1. Anderson AW, Gore JC. Analysis and correction of motion artifacts in diffusion weighted imaging. Magnetic resonance in medicine. 1994;32(3):379-87.
2. Butts K, de Crespigny A, Pauly JM, Moseley M. Diffusion-weighted interleaved echo-planar imaging with a pair of orthogonal navigator echoes. Magnetic resonance in medicine. 1996;35(5):763-70.
3. Miller KL, Pauly JM. Nonlinear phase correction for navigated diffusion imaging. Magnetic resonance in medicine. 2003;50(2):343-53.
4. Porter DA, Heidemann RM. High resolution diffusion-weighted imaging using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging, parallel imaging and a two-dimensional navigator-based reacquisition. Magnetic resonance in medicine. 2009;62(2):468-75.
5. Holdsworth SJ, Skare S, Newbould RD, Bammer R. Robust GRAPPA-Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Readout-Segmented (RS)-EPI. Magnetic resonance in medicine : official journal of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine / Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2009;62(6):1629-40.
6. Jeong H-K, Gore JC, Anderson AW. High-resolution human diffusion tensor imaging using 2-D navigated multishot SENSE EPI at 7 T. Magnetic resonance in medicine. 2013;69(3):793-802.
7. Ma X, Zhang Z, Dai E, Guo H. Improved multi-shot diffusion imaging using GRAPPA with a compact kernel. NeuroImage. 2016;138:88-99.
8. Dai E, Ma X, Zhang Z, Yuan C, Guo H. The Effects of Navigator Distortion Level on Interleaved EPI DWI Reconstruction: A Comparison Between Image and K-Space Based Method. Proceedings of the 24th Annual Meeting of ISMRM; 2016; Singapore.
Figures