1821
Value of the Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI in Pretreatment Predicting and Monitoring the Early Response to Chemoradiotherapy in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinomafei ping li1, zhongping zhang2, and Xiaoping Yu1
1Hunan Cancer Hospital, Changsha, People's Republic of China, 2MR Research China, GE Healthcare, Beijing, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
Chemoradiotherapy (CRT) was considered to be a very effective treatment regimen for locally advanced or unresectable esophageal cancer (EC). Usually the therapy-induced early changes of tumor microenvironment were prior to morphological changes, which cannot be detected by traditional imaging techniques. This study used intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging (IVIM-DWI) to investigate the early response to CRT in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). It was found that the IVIM-DWI parameters (ADC and D) might be valuable in pretreatment predicting and monitoring the early treatment response to CRT in ESCC.
Introduction
Chemoradiotherapy (CRT) was considered to be a very effective treatment regimen for locally advanced or unresectable EC, which may benefit the survival rate (1, 2). However, not all patients benefit equally from the CRT, as patient’s outcome mainly depends on the response to chemotherapy or radiotherapy (2-4). Therefore, early prediction of therapeutic response is important for making appropriate and timely adjustments to therapy regimens. Conventional diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) has been proved to be potentially helpful in predicting the response to CRT in EC (5-9). However, the predicting potency of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) derived from conventional DWI was inconsistent across different studies (6, 10, 11). In recent years, some studies have demonstrated that IVIM-DWI has an advantage over conventional DWI in predicting the therapeutic response for a variety of tumors(10, 11, 12). However, the application of IVIM-DWI to evaluate early response to CRT for EC has not been reported. The esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the main type in China (14]. Therefore, the purpose of our study was to investigate the reliability and feasibility of IVIM-DWI parameters in predicting the early response to CRT in patients with ESCC.Methods
Twenty-three ESCC patients who received CRT underwent an IVIM-DWI on a 1.5-Tesla MRI scanner at three time points (before CRT, at the time of 20Gy, and immediately after CRT). IVIM-DWI was applied with a single-shot diffusion-weighted spin-echo echo-planar (SS-SE-DW-EPI) sequence (TR/TE 6000 ms/76.8 ms, slice number 24, 5mm slice thickness, 1mm slice gap, FOV 40cm×30cm, matrix 128×130, NEX 4), with twelve b values (0, 10, 20, 30, 50, 80, 100, 150, 200, 400, 600, and 800s/mm2). After CRT, the patients were divided into the responders(complete response or partial response) and nonresponders(stable disease), according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) 1.1 guidelines. The mean values of IVIM-derived metrics (ADC, D, D* and f) and their percentage changes at different time points were compared between the responders and nonresponders. The diagnostic efficacy of the IVIM-DWI parameters was determined by using receiver-operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis.Results
For all 23 patients, the ADC and D values increased significantly throughout the course of the CRT(P<0.05), and the f value at the end of CRT showed significant increase (all P<0.05),as shown in table 1. The responders exhibited lower ADCpre, Dpre, ADC20Gy and D20Gy values, and higher ΔADC20Gy and ΔDpost than the nonresponders(all P<0.05),as shown in table 2, Figure1 and Figure2. The Dpre value had the highest sensitivity (100%) and relatively higher AUC value (0.865) in differentiating the responders from nonresponders,as shown in table 3.Discussion and conclusion
Our study demonstrated that both ADC and D values for all subjects increased significantly over the course of CRT. The findings can be explained by the destruction of tumor structure integrity in response to effective therapy, with necrosis, apoptosis, and cellularity reduction. Before CRT, the diffusion-related parameters (ADCpre and Dpre) showed negative correlations with the tumor regression ratio, and the responders had lower ADCpre and Dpre values than the nonresponders, indicating that pretreatment IVIM-DWI diffusion-related parameters may have potential in predicting the response to CRT for ESCC. The lower baseline ADC and D values might indicate higher cellular density, less necrosis, and more abundant vascularization which means higher perfusion and less hypoxia, and therefore would demonstrate more sensitivity to CRT. There were significant differences in the diffusion-related parameters (i.e., ADC20Gy, D20Gy and ΔADC20Gy) between the responders and nonresponders at the time of 20Gy, suggesting that the IVIM-DWI diffusion-related parameters can early differentiate the responders from the nonresponders. Thereby, adjustment of therapeutic strategy will be considered to the nonresponders so as to avoid ineffective treatment. There were no obvious differences observed in D* and f values, indicating that the perfusion-related parameters (D* and f) derived from IVIM-DWI may be useless in evaluating the therapeutic effect. Therefore, the impetus of this study was that the diffusion-related parameters derived from IVIM-DWI could predict and evaluate the early therapeutic response to CRT for ESCC patients.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Sjoquist KM, Burmeister BH, Smithers BM, et al. Survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy for resectable oesophageal carcinoma: an updated meta- analysis. Lancet Oncol 2011;12:681-692. 2. Donahue JM, Nichols FC, Li Z, et al. Complete pathologic response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer is associated with enhanced survival. Ann Thorac Surg 2009;87:392-398. 3. Allum WH, Stenning SP, Bancewicz J, Clark PI, Langley RE. Long-term results of arandomized trial of surgery with or without preoperative chemotherapy in esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2009;27:5062–5067. 4. Sakai M, Sohda M, Miyazaki T, et al. Usefulness of 18f-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography for Predicting the Pathological Response of Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy for T4 Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 2015;62:898-901. 5. Aoyagi T, Shuto K, Okazumi S, Shimada H, Kazama T, Matsubara H. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values Measured by Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Predict Chemoradiotherapeutic Effect for Advanced Esophageal Cancer. Dig Surg 2011;28: 252-257. 6. van Rossum PS, van Lier AL, van Vulpen M, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the prediction of pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in esophageal cancer. Radiother Oncol 2015;115:163-170. 7. De Cobelli F, Giganti F, Orsenigo E, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficient modifications in assessing gastro-oesophageal cancer response to neoadjuvant treatment: comparison with tumour regression grade at histology. Eur Radiol 2013;23:2165-2174. 8. Imanishi S, Shuto K, Aoyagi T, Kono T, Saito H, Matsubara H. Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Predicting and Detecting the Early Response to Chemoradiotherapy of Advanced Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Dig Surg 2013;30: 240-248. 9. Park SH, Moon WK, Cho N, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging: pretreatment prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. Radiology 2010;257: 56–63. 10. Chen Y, Liu X, Zheng D, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for early response assessment of chemoradiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Magn Reson Imaging 2014; 32:630-637. 11. Xiao-Ping Yu, Jing Hou, Fei-Ping Li, et al. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MRI for Predicting Early Response to Induction Chemotherapy and Chemoradiotherapy in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. J Magn Reson Imaging 2016; 45:1179-1190. 12. Gaeta M, Benedetto C, Minutoli F, et al. Use of Diffusion-weighted Intravoxel Motion and Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MR Imaing in the Assessment of Response to Radiotherapy of Lytic Bone Metastases from Breast Cancer. Acad Radiol 2014;21:1286-1293. 13. Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med 2003;349:2241-2252.Figures
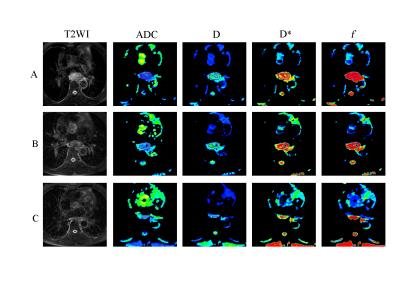
FIGURE 1: Representative images of an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patient with partial response (PR) in the responders. The first row (A) images are T2WI, ADC, D, D* and f maps before CRT. Images in the second row (B) are T2WI, ADC, D, D*, and f maps at the time of 20Gy. Images in the third row (C) are T2WI, ADC, D, D*, and f maps after CRT.
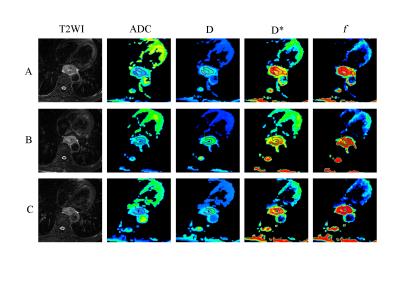
FIGURE 2:
Representative images of an esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patient with
stable disease (SD) in the nonresponders. The first row (A) images are T2WI,
ADC, D, D* and f maps before CRT. Images in the second row (B) are T2WI, ADC, D, D*, and f maps at the time of 20Gy. Images in the third row (C) are T2WI, ADC, D, D*, and f maps after CRT.
TABLE1. Changes of IVIM-DWI parameters throughout the course
of CRT.
TABLE2.
The IVIM-DWI parameters differences between the responders and nonresponders.
TABLE3. Diagnostic efficacy of IVIM-DWI
parameters in differentiation between the responders and nonresponders