1818
Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging of the Liver: Influence of Combined Respiratory-cardiac Triggering Method on Signal-to-noise Ratio and Repeatability of Quantitative Parameters1Radiology, Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, People's Republic of China, 2Radiology, Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, 3Philips Healthcare
Synopsis
As extremely susceptible to various kinds of motions, diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging always leads to insufficient image quality and poor reproducibility of quantitative measurements, especially for the liver. However, the use of combined respiratory-cardiac triggering, sychronizing data acquisitions with respiratory and cardiac cycles, could effective improve the signal-to-noise ratio and the repeatability of apparent diffusion coefficient and intravoxel incoherent motion parameters in the liver compared with respiratory triggering and free breathing without triggering method.
INTRODUCTION
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI) and its quantitative parameters, apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) parameters, have been validated as useful tools for evaluating diffuse liver diseases, characterizing focal lesions, and assessing treatment response of liver malignancies1-2. However, as extremely susceptible to various kinds of motions, DWI always leads to insufficient image quality and poor reproducibility of quantitative measurements, especially for the liver3. As many previous studies have demonstrated the significant influence of respiratory motion and cardiac pulsation on liver DWI4-5, we hypothesized that the use of combined respiratory-cardiac triggering (RCT), sychronizing data acquisitions with respiratory and cardiac cycles, might be an effective optimization method for liver DWI. Therefore, the aim of this study is to investigate whether the use of RCT method could improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and the repeatability of ADC and IVIM parameters in the liver DWI by comparing with respiratory triggering (RT) and free breathing (FB) without triggering.METHODS
In this prospective study, twelve healthy volunteers ( six males, six females; mean age, 26 years) were performed three liver DWI sequences twice respectively with RT, RCT, and FB method at a 3.0-T Ingenia MR imaging system (Philips, Best, the Netherland): single-shot spin-echo echo-planar imaging sequence, nine b values (0, 20, 40, 70, 100, 150, 200, 500, 800 sec/mm2). For RCT DWI, the trigger delay was set to 500 msec to maintain good image quality for upper abdominal organs, according to previous studies6 and volunteer’s heart rate (mean, 63 bpm; range, 55–70 bpm). Mean acquisition window was 458.4 msec (range, 357.1–590.9 msec). Mean acquisition time for RT DWI, RCT DWI, and FB DWI was 7.0 min (rang, 6–9 min), 8.3 min (range, 6–11 min), and 1.4 min respectively. The interval between two DWI sessions was 5 min. Fifteen regions of interest (ROIs) were respectively placed on six regions of the liver to measure ADC and IVIM parameters, including pure diffusion coefficient (D), perfusion fraction (f), and perfusion-related diffusion coefficient (D*). Signal intensity of each ROI was also recorded to calculate SNR at each b value. The repeatibility of ADC and IVIM parameters were evaluated by using the coefficient of variation (CV) across ROIs, within-subject CV and intraclass correlation coefficient across six liver regions and two sessions. The differences of SNR and quantitative parameters between three DWI techniques were evaluated with repeated-measures analysis of variance.RESULTS
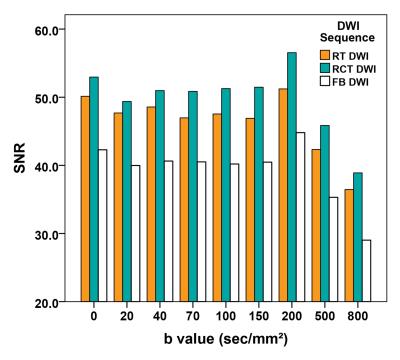
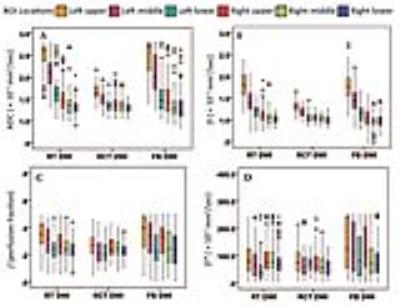
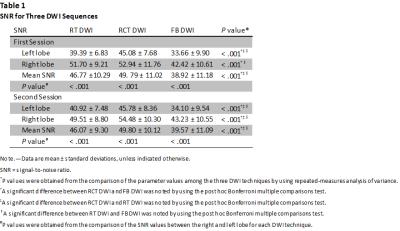
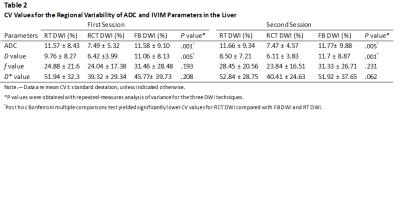
RCT DWI led to significantly enhanced SNR at each b value compared with RT DWI and FB DWI (P≤.001) (Fig. 1), and the improvement was more obvious in the left liver lobe (Table 1). RCT also resulted in lower CV of quantitative parameters across ROIs than RT DWI and FB DWI, which is significant for ADC and D values, especially for the left liver lobe (P≤.005) (Table 2, Fig. 2). Inter-examination reproducibility of ADC and IVIM parameters were the highest in RCT DWI (ICC, 0.535―0.885; within-subject CV 6.02%―47.47%), and were the lowest in FB DWI (ICC, 0.361―0.733; within-subject CV 19.36%―64.54%).DISCUSSION
The results of this study demonstrated that RCT double-triggering technique is a more effective optimization scheme than RT DWI or FB DWI without triggering to acquire higher SNR and repeatability of ADC and IVIM parameters. First, the application of RT method obviously improved the SNRs and the inter-examination repeatability for ADC and IVIM parameters than FB without triggering. Second, the addition of cardiac triggering to simply RT DWI could further improve the heart-related lower SNRs, regional variability, and even inter-examination variability of the quantitative measurements.CONCLUSION
RCT double-triggering technique is an effective optimization method for improving SNR and measurement repeatability of ADC and IVIM parameters in the liver compared with RT and FB without triggering method.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Bruegel M, Holzapfel K, Gaa J, et al. Characterization of focal liver lesions by ADC measurements using a respiratory triggered diffusion-weighted single-shot echo-planar MR imaging technique. Eur Radiol. 2008;18(3):477-85.
2. Yamada I, Aung W, Himeno Y, Nakagawa T, Shibuya H. Diffusion coefficients in abdominal organs and hepatic lesions: evaluation with intravoxel incoherent motion echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology. 1999;210(3):617-23.
3. Taouli B, Koh DM. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the liver. Radiology. 2010;254(1):47-66.
4. Dyvorne HA, Galea N, Nevers T, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver with multiple b values: effect of diffusion gradient polarity and breathing acquisition on image quality and intravoxel incoherent motion parameters--a pilot study. Radiology. 2013;266(3):920-9.
5. Lee Y, Lee SS, Kim N, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the liver: effect of triggering methods on regional variability and measurement repeatability of quantitative parameters. Radiology. 2015;274(2):405-15.
6. Binser T, Thoeny HC, Eisenberger U, Stemmer A, Boesch C, Vermathen P. Comparison of physiological triggering schemes for diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in kidneys. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;31(5):1144-50.
Figures