1776
Characteristic analysis of in vivo and ex vivo rat brains by 7.0 T DTI MR1Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Chengdu, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
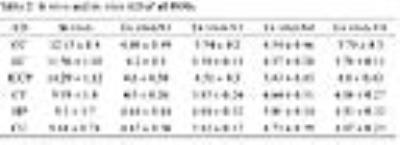
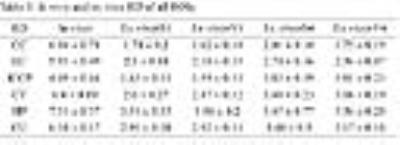
Ex vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) are widely used in experimental studies for excellent images. The comparison between in vivo and ex vivo DTI has been conducted without the same scan parameters. We aimed to compare the living and fixed white and gray matters under the same condition and explore the effects of coil and signal average. Diffusivities were significant different between living and fixed brains. Coil and signal average significantly affected the signal-to-noise ratio of ex vivo white and gray matters. The results indicate that fixation and MR conditions should be considered in clinical and experimental DTI studies.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Sun SW, Neil JJ, Song SK. Relative indices of water diffusion anisotropy are equivalent in live and formalin-fixed mouse brains. Magn Reson Med. 2003;50(4):743-748.
2. Rane S, Duong TQ. Comparison of in vivo and ex vivo diffusion tensor imaging in rhesus macaques at short and long diffusion times. Open Neuroimag J. 2011;5(172-178.
3. Wu D, Xu J, McMahon MT et al. In vivo high-resolution diffusion tensor imaging of the mouse brain. Neuroimage. 2013;83(18-26.
4. Werner M, Chott A, Fabiano A et al. Effect of formalin tissue fixation and processing on immunohistochemistry. Am J Surg Pathol. 2000;24(7):1016-1019.
5. Quester R, Schroder R. The shrinkage of the human brain stem during formalin fixation and embedding in paraffin. J Neurosci Methods. 1997;75(1):81-89.
6. Wehrl HF, Bezrukov I, Wiehr S et al. Assessment of murine brain tissue shrinkage caused by different histological fixatives using magnetic resonance and computed tomography imaging. Histol Histopathol. 2015;30(5):601-613.
7. Madi S, Hasan KM, Narayana PA. Diffusion tensor imaging of in vivo and excised rat spinal cord at 7 T with an icosahedral encoding scheme. Magn Reson Med. 2005;53(1):118-125.
8. Le Bihan D. Diffusion and perfusion magnetic resonance imaging-applications to functional MRI. New York: Raven Press. 1995;
9. Bittersohl B, Huang T, Schneider E et al. High-resolution MRI of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) at 3T: comparison of surface coil and volume coil. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;26(3):701-707.
Figures