1771
Abnormal white matter integrity in parkinson’s disease patients with cognitive impairment revealed by tract-based spatial statistics1Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang, China, Guiyang, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
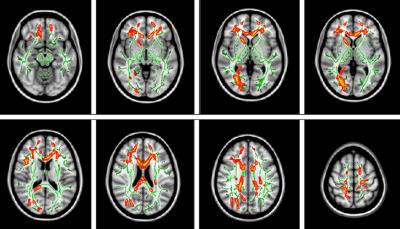
Results from recent neuroimaging studies suggest that PD patients with cognitive impairment(PDCI) is associated with abnormal white matter integrity. In this study, we used tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) method combined with diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to investigate the microstructural integrity of the white matter in PDCI. Results from TBSS demonstrated that PDCI patients had significantly lower FA than healthy controls in anterior thalamic radiation(atr), corticospinal tract (cst), cingulated gyrus(cg), forceps minor(fi), the right inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus(ifo), inferior longitudinal fasciculus(ilf), superior longitudinal fasciculus(slf) and uncinate fasciculus(uf). There were no white matter integrity changes in PD patients without cognitive dysfunction, And also significantly correlation was found between FA in the right ifo and MoCA scores.
parkinson’s disease, cognitive impairment, diffusion tensor imaging,tract-based spatial statistics
Introduction Cognitive dysfunction is common in Parkinson's disease (PD). Results from recent neuroimaging studies suggest that brain changes associated with cognitive impairment in PD have focused on grey matter atrophy, cortical thickness alterations [1,2]. Little is known about the impact of PD on the integrity of the white matter of the brain. In this study, we used tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) method combined with diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to investigate the microstructural integrity of the white matter in PD patients with cognitive impairment.
Materials and Methods Subjects: 22 PD patients without cognitive impairment( PDN) , 18 PD patients with cognitive impairment( PDCI) and 22 age matched healthy controls were recruited from the community by advertisements. All PD patients had been diagnosed by neurologists , and they had no history of any psychiatric or neurological diseases. All participants underwent MMSE and MoCA test to assess cognitive dysfunction. Image acquisition: MRI was performed on a Philips 3 T Achieva MR scanner with an 8-channel phased array coil. The DTI involved sequential single-shot spin-echo planar imaging sequence in contiguous axial planes covering the entire brain. The diffusion sensitizing gradients were applied along 32 non-collinear directions, together with acquisition without diffusion weighting (b=0). The imaging parameters were shown as follows: TR=5003 ms, TE=70 ms, average=3, b-value=800 s/mm2, slice thickness=3.0 mm, 45 slices. The matrix size was 160×160 and reconstructed to 256×256 with a resolution of 1.38×1.38×3.00 mm3. Data analysis: The images of FA were subjected to TBSS using the FMRIB software library (FSL 5.0; http://fsl.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/fsl/fslwiki/), for a detailed description, see Smith et al[3]. volume-of-interest (VOI) analysis of the TBSS results was performed to investigate the relationship between changes in FA and axial diffusivity (Da )and radial diffusivity(Dr).
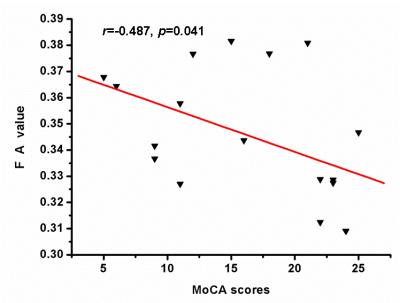
Results TBSS demonstrated that PDCI patients had significantly lower FA than healthy controls in anterior thalamic radiation(atr), corticospinal tract (cst), cingulated gyrus(cg), forceps minor(fi), the right inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus(ifo), inferior longitudinal fasciculus(ilf), superior longitudinal fasciculus(slf) and uncinate fasciculus(uf). (Figure 1). There were no white matter integrity changes in PDN. VOI analysis showed decreased FA in this region as reflected by decreased Da and increased Dr(data not show). Importantly, we found there was significantly correlation between FA in the right ifo and MoCA scores (r=-0.487, p=0.041) (Figure 2).
Discussion In this study, we used TBSS to examine the integrity of white matter microstructure in PD with cognitive impairment. We found PDCI patients had reduced FA mainly in anterior thalamic radiation(atr), corticospinal tract (cst), cingulated gyrus(cg), forceps minor(fi), the right inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus(ifo), Inferior longitudinal fasciculus(ilf), superior longitudinal fasciculus(slf) and uncinate fasciculus(uf). The widespread deterioration of cerebral white matter in the PDCI group agrees with the results of the previous study[4-5]. VOI analysis showed decreased FA in theses regions as reflected by decreased Da and increased Dr, which was probably caused by axonal loss and disrupted integrity of myelin [6]. Furthermore, correlation findings suggest that cognitive decline is associated with decreased microstructural integrity of the right inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus, which indicates that DTI may be used as a qualified objective tool to evaluate the cognitive status of PD patients. Further investigations are required to determine the relationship between white matter damages, the functional network of PD patients with cognitive impairment.
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of China (8156070059) and Science and Technology Department of Guizhou Province-Guizhou medical university, Qiankehe LG[2012]024.References
[1] Mov Disord. 2011 Feb 1;26(2):289-96. [2] PLoS One. 2013 May 22;8(5):e64222. [3] NeuroImage. 2006; 31: 1487-1505. [4] Hum Brain Mapp. 2012 Mar;33(3):727-39. [5] Eur Radiol (2013) 23:1946–1955. [6] Neuroimage, 20: 1714-1722, 2003.Figures