1449
Diagnostic performance of texture analysis on MRI in differentiated degree of head and neck carcinoma1Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
The aim of this study was to determine the diagnostic accuracy of pathological differentiated degree of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) using MRI texture analysis. The following texture analysis parameters were derived from the T1WI, T2WI , T2fs and Post-Gad T1WI based on different scale: entropy , mean pixel intensity, standard deviation(SD), skewness, and kurtosis. ROC curves and AUC of each parameter was determined, respectively. We conclude that the entropy at fine texture scale on Post-Gad T1WI had the best ability .
Purpose
To determine the diagnostic accuracy of pathological differentiated degree of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) using MRI texture analysis.Methods and materials
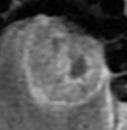
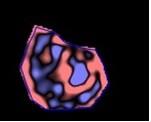
45 patients histologically confirmed locally advanced SCC of the head and neck were retrospectively enrolled this study. Clinical data from the medical records database were gathered, including patients demographic information (age, sex, and race),social factors (alcohol and tobacco use), T stage, N stage, overall stage and clinical stage. Imaging was performed on MR imaging systems operating at two 1.5T scanner (n=25) and one 3.0T scanner (n=20). Contrast-enhanced images were obtained following intravenous (IV) administration of 0.2 ml/kg of Gadopentetate Dimeglumine (BEILU pharmaceutical co., LTD, Beijing, China). Standard clinical MR images were used, including the following that were subsequently used for texture analyasis: axial T1-weighted imaging (T1WI), T2-weighted imaging (T2WI), T2-weighted imaging with fat saturation (T2WI-fs), axial T1WI with gadolinium (Post-Gad T1WI). The MRTA was assessed using a commercially available research software program (TexRAD) [1]that applies a filtration-histogram technique for characterizing tumor histological degree. Filtration step selectively filters and extracts texture features at different anatomical scales varying from 2mm (fine features) to 6 mm (coares features), the entropy and histogram analysis parameters (mean pixel intensity, standard deviation(SD), skewness, and kurtosis) was obtained. ROC was performed to assess sensitivity and specificity for differentiating between the different degrees and calculating a threshold value to quantify the heterogeneity. The areas under the curve (AUC) for texture analysis parameters to distinguish defined tumor grades were calculated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. The optimal thresholds and their determined sensitivity and specificity were reported. Positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) was also calculated from the ROC analysis. The lead statistician performing the statistical analysis was H.W., a PhD biostatistician with 6 years of experience. All statistical significance was set to 5% and was performed on SPSS software (IBM SPSS, version 17, SPSS Inc. Chicago, IL, USA). [2, 3]
Results
Lower to moderate and moderated to well differentiated degree of SCC was best discriminated using entropy at fine texture scale on Post-Gad T1WI, with a sensitivity and specificity of 90.9% and 66.7% (AUC 0.742, P=0.049).Conclusion
Measuring heterogeneity in head and neck SCC to discriminate Lower to moderate and moderated to well differentiated degree using MRTA can be a useful tool to agreement the diagnostic accuracy in grading SCC and potentially hasten treatment decisionAcknowledgements
Thank you for the support from Professor Balaji Ganeshan, Institute of Nuclear Medicine, University College London, University College Hospital.References
1] Zhang H, Graham CM, Elci O, et al. Locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: CT texture and histogram analysis allow independent prediction of overall survival in patients treated with induction chemotherapy. Radiology. 2013. 269(3): 801-9.
[2] Skogen K, Schulz A, Dormagen JB, Ganeshan B, Helseth E, Server A. Diagnostic performance of texture analysis on MRI in grading cerebral gliomas. Eur J Radiol. 2016. 85(4): 824-9.
[3] Worsham MJ, Stephen JK, Lu M, et al. Disparate molecular, histopathology, and clinical factors in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma racial groups. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012. 147(2): 281-8.
Figures