1359
In vivo MR blood oximetry based on $$$T_2$$$-prepared bSSFP1Radiology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States, 2Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States
Synopsis
To develop in vivo MR oximetry based on T2-prepared bSSFP constant refocusing-pulse interval ($$$\tau_{180}$$$) T2-preparation, three-parameter signal fitting for T2 extraction and magnetization reset for shortened pulse sequence cycle were implemented and evaluated against a multi-spin echo sequence using static and flowing MnCl2 solutions with known T2 values. The whole-blood T2 was also quantified to investigate the effect of varying . The phantom results support three-parameter fitting, and <5% error incurred in T2 quantification with shortened T2-preparation cycle and presence of constant flow. Approximately 10% longer whole-blood T2 was observed with constant relative to varying .
Introduction
In vivo whole-blood oxygenation level can be derived from a measurement of T2 of blood water protons [1]. Compared to the original approach of Wright et al [1] a T2-prepared balanced SSFP (T2-bSSFP) is appealing due to superior SNR efficiency and acquisition speed. T2-bSSFP had previously been developed to address limitations of T2-weighted imaging of myocardial edema [2]. Typically, magnetization preparation involves four non-selective composite refocusing pulses with MLEV-4 phase cycling [3], and the inter-refocusing pulse interval ($$$\tau_{180}$$$) is stepped to vary TE. The data is then fitted to a two-parameter mono-exponential decay equation to estimate T2. Here, we adapted the T2-bSSFP approach to more closely match the Luz-Meiboom model of transverse relaxation in the presence of chemical exchange [4] and data acquisition with bSSFP for in vivo quantification of HbO2 saturation for a wide range of applications, including estimation of placental and fetal oxygen consumption rate [5].Methods
Protocol and analysis
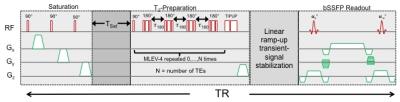
The semi-empirical Luz-Meiboom model relating to HbO2 demands that be held constant for all T2-preparation durations or TEs. The updated T2-preparation (Fig 1) comprises integer multiples of MLEV-4 cycles to vary TEs [1], and T2 is extracted by three-parameter fitting since the T2-prepared bSSFP transient signal approaches a steady-state instead of zero [6]. Further, immediately following the bSSFP readout the magnetization is reset via saturation and allowed to recover for a period of TSat seconds to reduce the interval between successive T2-preparation and therefore shortened TR for faster T2 quantification.
Phantom study: 2- vs. 3-parameter fitting T2 was quantified with constant refocusing-pulse interval ($$$\tau_{180}$$$-fixed) T2-bSSFP (see below) and multi-spin echo pulse sequences in four MnCl2 solutions of different concentration (nominal T2 values ranging from 105 to 200ms); TSat was varied from 1.5 to 3.5 sec. T2 was also measured in the presence of constant flow speeds (5 to 28cm/s) with one of the prepared MnCl2 solutions (T2=135 ms).
In vivo venous blood T2 quantification: fixed vs. varying $$$\tau_{180}$$$
Venous blood T2 quantification in the superior sagittal sinus (SSS) was performed in four subjects using the T2-bSSFP pulse sequence with fixed and varying . The SSS was targeted for its moderate pulsatility and low average velocity (~20 cm/s).
Imaging parameters
All studies were performed on a 1.5T system (Siemens Avanto) with a 12-channel head coil.
T2-preparation
As shown in Fig 1, after magnetization reset and TSat (varying from1.5 to 3.0 sec) T2-preparation is initiated with a 90o RECT excitation pulse, followed by MLEV-4 type refocusing pulses with =12ms, and composite tip-up (270x360-x). The T2-bSSFP version of [2] has one MLEV-4 and increases to control TE, and TR is set to 4s, resulting in 20s acquisition time for five echoes.
bSSFP
FOV 307mm, slice thickness 8mm, TE/TRbSSFP=2/4 ms, flip angle 60o, in-plane resolution 0.8mm, half-Fourier with linear ramp-up signal stabilization and 14 reference lines for reconstruction phase correction, i.e. the k-space center traversed on 25th pulse cycle.
Multi-spin echo
FOV 170mm, slice thickness 5mm, TEs=6.7, 48, 96, 144, 192ms, TRSE=3000 ms, flip angle 90o, in-plane resolution 0.9mm, partial-Fourier factor 5/8.
T2 estimation
T2 values were quantified by fitting the average ROI pixel intensities from each of the five images to either a two- or three-parameter equation, i.e. Ae-Bt or Ae-Bt+C. Corrected TEs were used to reduce the error associated with T1 decay between RECT pulses [7].
Results
Phantom study
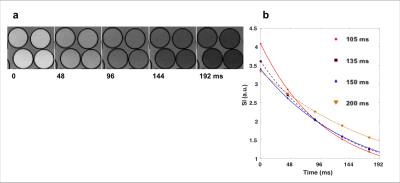
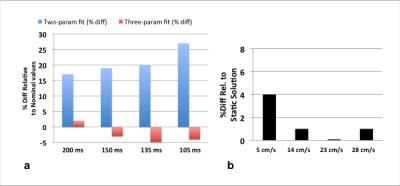
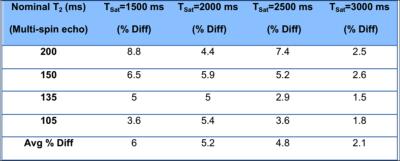
Sample images of MnCl2 solutions acquired with T2-bSSFP are shown in Fig 2. The bias introduced with two-parameter fitting is summarized in Fig 3a. Shorter TSat led to a modest reduction in accuracy as a result of lower SNR (Table 1). Fig 3b suggests signal enhancement from steady flow (as high as 28 cm/s) does not affect the accuracy of T2 quantification.
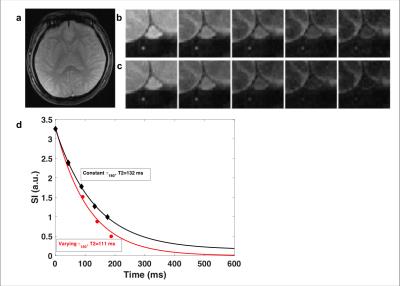
Fig 4 shows sample in vivo images of the SSS in a healthy subject and the bias in the signal decay profile between fixed and varying . If we use the calibration curve of Wright et al [1] T2=132 and 111 ms translate to blood oxygenation of 62 and 55 %HbO2, respectively. The average bias in estimated T2 was approximately 10% (longer with fixed relative to variable ). Data analysis (not shown) indicates that when is varied two- and three-parameter fit gives the same T2 value.
Conclusions
The proposed T2-prepared bSSFP sequence and analysis method is shown to be reproducible and robust to variations in flow speed and should therefore be suited for blood oximetry.Acknowledgements
NIH Grants K25 HL111422 and U01 HD087180 supported this work.References
[1] Wright et al, JMRI 1991, [2] Giri et al, JCMR 2009, [3] Levitt et al, JMR 1981, [3], [4] Luz et al, J Chem Phys 1963, [5] Sun et al, Circulation 2015, [6] Akcakaya et al, MRM 2015, [7] Foltz et al, MRM 1997.Figures