1010
Machine learning analysis of multi-parametric MRI helps to improve the predictive performance in prostate cancerRui Wang1 and Xiaoying Wang1
1Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
We first investigated the systemic outcome of a crowd underwent PSA-based screening and pre-biopsy mp-MRI, and demonstrated the predictive role of pre-biopsy mp-MRI for PCa by using an advanced machine learning-based approach. Here we answer one important question at the beginning of the paper: (1) mp-MRI coupled with PSA screening program can be used to detect PCa. By the constructed nomogram, the outcome of most patients could be accurately predicted in the first 1-yr follow-up period if they received a pre-biopsy mp-MRI examination, even without invasive TRUS biopsy.
Background
PSA-based screening has come in for a lot of criticisms due to noticeable false positive results for prediction of prostate cancer (PCa).Purpose
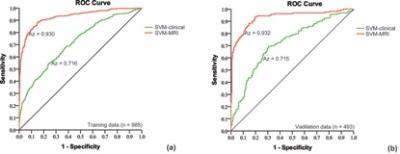
To investigate whether a machine learning analysis of multi-parametric (mp) MRI can help to improve the predictive performance in PCa.Design, setting, and participants
Based on a support vector machine classification analysis, we modeled clinical data (age, PSA, DRE, TRUS, PSAD, prostate volume) and mp-MRI findings on 985 men between Jan 2002 and Dec 2009 to predict the probability of PCa. The model was validated on 493 patients treated at a same institution during the same period. Median follow-up in the training and validation cohorts was 40 and 38 mo, respectively.Measurements
5-yr rate of PCa were measured.Results and limitations
At 5-yr follow-up period, 34.3% of patients had systemic progression of PCa. By adding mp-MRI findings, the machine learning-based model increased area under curve (Az) from 0.715 to 0.938 (p < 0.001), sensitivity from 27.4% to 83.5% (p < 0.001), positive predictive value (PPV) from 57.7% to 77.4% (p = 0.004), and negative predictive value (NPV) from 71.3% to 91.5% (p < 0.001). Scaled by PSA level, the model had high PPV (93.6%) in patients with PSA > 20 ng/ml, while with intermediate to low PPVs in group of PSA 10-20 ng/ml (64%), PSA 4-10 ng/ml (55.8%) and PSA 0-4 ng/ml (29%). Among all predictors, MR PI-RADS score had the highest Cox hazard ratio (2.112; p < 0.001) associated with time to progression of PCa, followed by PSA (1.435; p < 0.001), age (1.012; p = 0.043).