0950
Earlier detection of breast cancer by abbreviated MRI screening using color intensity projections (CIP) applied to high spatiotemporal resolution imaging1Physics and Medical Technology, VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2Radiology, VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 3Radiotherapy, VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Synopsis
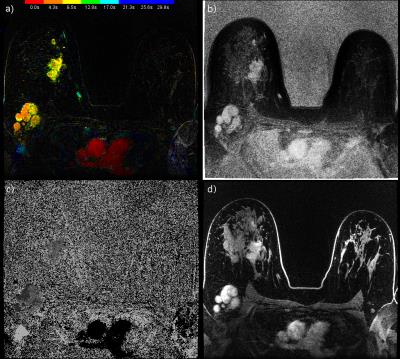
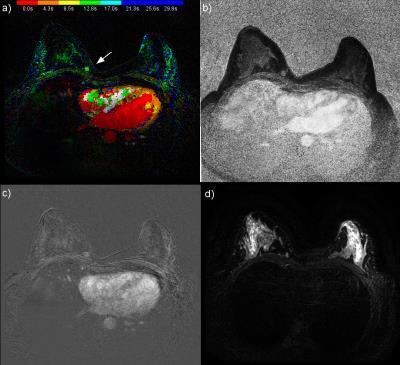
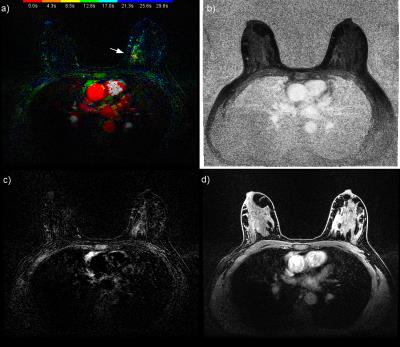
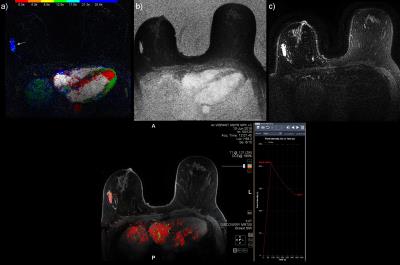
Dynamic contrast enhancement (DCE) MRI is more sensitive than X-ray based mammography for detecting breast cancer especially for the 10% of women with extremely dense breasts. However, full diagnostic protocol (FDP) MR exams are too expensive for screening. Recent abbreviated MR protocols - which require only one quarter of the acquisition time - use high spatial temporal resolution (HSTR) sequences that generate thousands of images. We found color intensity projections (CIP) reduces radiologist reading time for detection of malignant tumours by visualizing their amount and time of enhancement (TOE) especially in combination with the value of the maximum slope (VMS).
Purpose
To perform a preliminary assessment of whether color intensity projections (CIP) [CoverKS2007] speeds up reading in breast cancer screening of the thousands of images generated by high spatial temporal resolution (HSTR) sequences without the use of specialized image viewing tools.
Background
Several studies have reported DCE-MRI to be more sensitive than X-ray based mammography for detecting breast cancer [KuhlCK2014, MangoVL2015]. The increased sensitivity allows tumours to be detected earlier when the disease is more treatable. Typical sensitivities quoted are 70% for mammography and 95% for MRI although for mammography it can be as low as 30% in for women with extremely dense breasts [EmausMJ2015, DOrsiCJ2013]. Compounding the problem, women with extremely dense breasts have a 4 to 6 fold higher risk of breast cancer than women with low density breasts. Unfortunately, MR has been too expensive to screen most women. To reduce screening costs many research institutes have studied “abbreviated” MR protocols that take just 10 to 15 minutes of scanner room time per patient [KuhlCK2014, MangoVL2015, MachidaY2016, JainM2016, GrimmLJ2015, HeacockL2016, MoschettaM2016] as compared to a typical 40 minute full diagnostic protocol (FDP). Recent studies have employed contrast enhancement kinetics with high spatial temporal resolution (HSTR) sequences [PlatelB2014, MannRM2014, AbeH2016, GotoM2016, MannRM2016] that acquire a whole volume of both breasts in under 5 seconds allowing the 50 second wash in interval of contrast agent to be imaged with high spatial resolution. HSTR sequences have demonstrated high sensitivity to breast tumours and high specificity in discriminating malignant and benign tumours. When time to enhancement (TOE) of a breast tumour is less than 8 seconds the tumour is likely malignant while longer than 16 seconds is likely benign [SardanelliF2000, PlatelB2014, GotoM2016]. However, HSTR sequences generate thousands of images per patient and thus are time consuming and costly for a radiologist to read and often require specialized and expensive image review software. Calculated from the HSTR images, the value of maximum slope (VMS) has been used to discriminate between benign and malignant tumours [PlatelB2014, MannRM2014]. T2 images are also helpful as benign tumours are usually bright while malignant are not.Methods
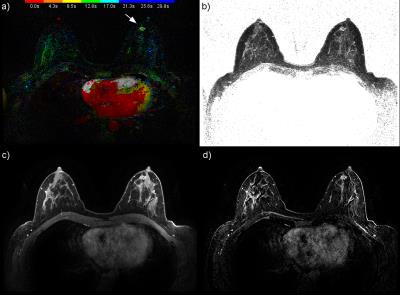
From January until October 2016 a total of 191 clinical patients - most of which were reviewed for this study - were scanned for breast cancer on a 3T GE Discovery 750 MR system with our FDP. Patients were referred for MRI both for screening of high risk of breast cancer and pre and post treatment scanning. This study was approved by our university's ethics board and informed consent waved. Our FDP included a series of T1 weighted images over 7 minutes as part of the standard enhancement kinetics, T2 weighted images with fat saturation, DWI, and a DISCO-DIXON HSTR sequence [SaranathanM2012]. During the 90 seconds of the HSTR sequence, every 4.26 seconds an image volume of both breasts was acquired with voxels of 0.66x0.66x2.20 mm for both fat and water images. Color intensity projections (CIP) - with the amount of enhancement encoded in the brightness and the TOE encoded in the hue - were calculated from the HSTR images [CoverKS2007]. The exams were reviewed for this study by an highly experienced breast radiologist (KMD).Results and Discussion
Five cases (Figures 1 to 5) were selected from the MR exams to demonstrate the promising results of reading HSTR images using the combination of CIP-TOE and VMS. The performance of the CIP-TOE and VMS compared to that of the FDP, in terms of reading time especially for negative exams and the detections of lesions, merits a formal study with several independent radiologists and detailed statistical evaluation. Also, no "show stoppers" were found for using CIP-TOE and VMS as part of an abbreviated breast screening protocol that uses only the T2 and DISCO sequences and non specialized image review software. Thus, further study is warranted.Conclusion
The results of this informal preliminary study provides encouraging evidence that the CIP-TOE visualization tool - in combination with VMS and without the use of specialized image viewing tools - can substantially reduce a radiologist reading time of the thousands of images generated by HSTR sequences in breast cancer screening. A more formal study with several independent radiologists is justified to confirm this result.Acknowledgements
The work has been funded by the VU University Medical Center in Amsterdam.References
AbeH2016. Abe H, Mori N, Tsuchiya K, Schacht DV, Pineda FD, Jiang Y, Karczmar GS. Kinetic Analysis of Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions With Ultrafast Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI: Comparison With Standard Kinetic Assessment. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016; Aug 17:1-8.
BoetesC1994. Boetes C, Barentsz JO, Mus RD, van der Sluis RF, van Erning LJ, Hendriks JH, Holland R, Ruys SH. MR characterization of suspicious breast lesions with a gadolinium-enhanced TurboFLASH subtraction technique. Radiology 1994;193:777-81.
BoetesC2011. Boetes C. Update on screening breast MRI in high-risk women. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2011; 38:149-58. BoydNF1998. Boyd NF, Lockwood GA, Martin LJ, Knight JA, Byng JW, Yaffe MJ, Tritchler DL. Mammographic densities and breast cancer risk. Breast Dis. 1998;10:113-26.
Cover KS, Lagerwaard FJ, van den Berg R, Buis DR, Slotman BJ. Color intensity projection of digitally subtracted angiography for the visualization of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 2007;60:511–515. CoverKS2007B. Cover KS, Lagerwaard FJ, Senan S. Color intensity projections: A simple way to display changes in astronomical images. Publ Astron Soc Pac 2007;119:523-526. CoverKS2008.
DOrsiCJ2013. D'Orsi CJ, Sickles EA, Mendelson EB, Morris EA, Bassett LW, Bohm-Velz M, Berg WA, Comstock CE, Lee CH.. ACR BI-RADS Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System. Reston, VA, American College of Radiology; 2013.
EmausMJ2015. Emaus MJ, Bakker MF, Peeters PH, Loo CE, Mann RM, de Jong MD, Bisschops RH, Veltman J, Duvivier KM, Lobbes MB, Pijnappel RM, Karssemeijer N, de Koning HJ, van den Bosch MA, Monninkhof EM, Mali WP, Veldhuis WB, van Gils CH. MR Imaging as an Additional Screening Modality for the Detection of Breast Cancer in Women Aged 50-75 Years with Extremely Dense Breasts: The DENSE Trial Study. Design Radiology 2015 Nov;277:527-37.
GotoM2016. Goto M, Takezawa K, Sakai K, Imai H, Elisabeth Weilandand E, Yamada K. Utility of Semi-Quantitative Analysis of Initial Enhancement Using TWIST-VIBE in the Diagnosis of Breast Lesions. Int Soc Magn Reson Med Conf Singapore 2016;405.
HeacockL2016. Heacock L, Melsaether AN, Heller SL, Gao Y, Pysarenko KM, Babb JS, Kim SG, Moy L. Evaluation of a known breast cancer using an abbreviated breast MRI protocol: Correlation of imaging characteristics and pathology with lesion detection and conspicuity. Eur J Radiol. 2016;85:815-23.
HuangW2011. Huang W, Tudorica LA, Li X, Thakur SB, Chen Y, Morris EA, Tagge IJ, Korenblit ME, Rooney WD, Koutcher JA, Springer CS Jr. Discrimination of benign and malignant breast lesions by using shutter-speed dynamic contrast enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 2011;261:394-403.
JainM2016. Jain M, Jain A, Hyzy MD, Werth G. FAST MRI breast screening revisited. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2016; Jul 27:12502. [Epub ahead of print]
KuhlCK2014. Kuhl CK, Schrading S, Strobel K, Schild HH, Hilgers RD, Bieling HB. Abbreviated breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): first postcontrast subtracted images and maximum-intensity projection-a novel approach to breast cancer screening with MRI. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:2304-2310.
MachidaY2016. Machida Y, Shimauchi A, Kanemaki Y, Igarashi T, Harada M, Fukuma E. Feasibility and potential limitations of abbreviated breast MRI: an observer study using an enriched cohort. Breast Cancer. 2016; Aug 2. [Epub ahead of print].
MandelsonMT2000. Mandelson MT, Oestreicher N, Porter PL, White D, Finder CA, Taplin SH, White E. Breast density as a predictor of mammographic detection: comparison of interval- and screen-detected cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000 Jul 5; 92(13):1081-7.
MangoVL2016. Mango VL, Morris EA, David Dershaw D, Abramson A, Fry C, Moskowitz CS, Hughes M, Kaplan J, Jochelson MS. Abbreviated protocol for breast MRI: are multiple sequences needed for cancer detection? Eur J Radiol. 2015;84:65-70.
MannRM2008. Mann RM, Kuhl CK, Kinkel K, Boetes C. Breast MRI: guidelines from the European Society of Breast Imaging. Eur Radiol. 2008;18:1307-18. MannRM2014. Mann RM, Mus RD, van Zelst J, Geppert C, Karssemeijer N, Platel B. A novel approach to contrast enhanced breast magnetic resonance imaging for screening high-resolution ultrafast dynamic imaging. Invest Radiol. 2014; 49:579-585.
MannRM2016. van Zelst J, Merida AG, Vreemann S, Dorrisus M, Duvivier KM, Lardenoije-Broker S, Lobbes M, Loo C, Veldhuis W, Veltman J, Karssemeijer N, Mann RM. Breast cancer screening with a high spatiotemporal MRI sequence in women at increased risk is as accurate as screening with a standard diagnostic MRI protocol. European Society of Breast Imaging Congress 2016; Paris, France: Sept 21-22.
MoschettaM2016. Moschetta M, Telegrafo M, Rella L, Stabile Ianora AA, Angelelli G. Abbreviated Combined MR Protocol: A New Faster Strategy for Characterizing Breast Lesions. Clin Breast Cancer 2016;16:207-11.
PlatelB2014. Platel B, Mus R, Welte T, Karssemeijer N, Mann R. Automated characterization of breast lesions imaged with an ultrafast DCE-MR protocol. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2014;33:225-232.
SardanelliF2000. Sardanelli F, Rescinito G, Giordano GD, Calabrese M, Parodi RC. MR dynamic enhancement of breast lesions: high temporal resolution during the first-minute versus eight-minute study. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2000; 24:724-31.
SaranathanM2012. Saranathan M, Rettmann DW, Hargreaves BA, Clarke SE, Vasanawala SS. DIfferential Subsampling with Cartesian Ordering (DISCO): a high spatio-temporal resolution Dixon imaging sequence for multiphasic contrast enhanced abdominal imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 2012;35:1484-92.
Figures