0873
The application of whole lesion IVIM analysis using iZOOM DWI in the diagnosis of thyroid tumor1Department of MR, Beijing Shijitan hospital of capital medical university, Beijing, People's Republic of China, 2Philips Healthcare (China), Beijing, People's Republic of China, 3Philips Healthcare (China), Suzhou, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
To explore the ability of IVIM parameters derived from iZoom DWI in differentiating malignant thyroid nodules from benign ones. 40 patients with 45 pathologically proven thyroid nodules were involved. iZOOM DWI with 2D RF was employed to decrease the distortion and carotid coil was used to increase the SNR. 3D ROI was drawn manually to cover the whole lesion. D and f values were significantly lower in malignant nodules than in benign nodules. According to ROC curve analysis IVIM almost reached the upper limit of the accuracy based on US.
Introduction
The reported incidence of thyroid cancer is up to 0.07% over the past 30 years. Ultrasonography (US) has been used as a first step in the assessment of thyroid nodules, but no single US criterion has been demonstrated to accurately differentiate benign nodules from malignant nodules. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is reported to be valuable in differentiating malignant and benign thyroid nodules1. The main challenge in applying DWI in the thyroid imaging is the artifact and distortion caused by the magnetic susceptibility. IZoom DWI, which has shorter echo train length by using a 2D RF, is less sensitive to the inhomogeneity of magnetic field23. Furthermore, compared to regular DWI model, Intravoxel incoherent motion(IVIM)model has the ability to separate tissue diffusivity from microcapillary perfusion4. However, the performance of IVIM parameters derived from iZoom DWI in differentiating thyroid nodules is undefined. Therefore, the purpose of our study is to assess whether IVIM parameters derived from iZoom can distinguish malignant thyroid nodules from benign ones.Purpose
To explore the usefulness of intravoxel incoherent motion(IVIM)parameters derived from iZoom diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in differentiating malignant and benign thyroid nodules, with postoperative pathological results as the reference standard.Methods
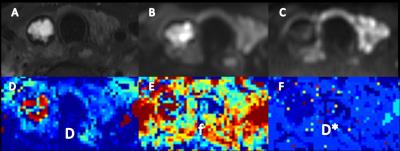
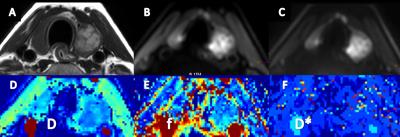
This retrospectively study included 40 patients(4 men, 36 women; mean age46.3 years; age range, 24-73 years)with 45 pathologically proven thyroid nodules greater than 5 mm in diameter. The postoperative pathological diagnosis included papillary thyroid cancer (n=23),nodular goiter(n=19),thyroid adenoma(n=2) and Hashimoto's thyroiditis(n=1). All patients underwent preoperative examinations (Philips 3.0T Ingenia, Philips Medical System, The Netherlands) with conventional and iZoom DWI sequences Using a 8-channel carotid coil. iZOOM DWI using 2D RF pulse was scanned with following parameters: TE/TR 69/1400ms, FOV 160x47mm, acquisition matrix 108x30, 10 slices with the thickness of 5mm and 1mm gap, NSA 4. 8 b values (0, 20, 50, 100, 200, 400, 600, 990) were used. The non-linear fitting of the bi-exponential model was performed on Matlab. A 3D ROI was manually drawn on multiple slices to cover the whole nodule by two radiologists blinded to pathological diagnosis and IVIM parameters(D, pure diffusion; f, perfusion fraction; D*, pseudo-diffusion) were measured . The IVIM parameters between malignant and benign thyroid nodules were compared by using independent samples t test. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was used to evaluate the diagnostic performance of IVIM parameters in differentiating benign nodules from malignancy. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) and the optimal cut-off values were calculated, meanwhile accuracy rate, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) was determined. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.Result
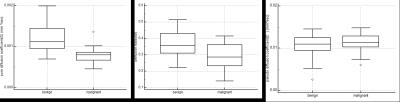
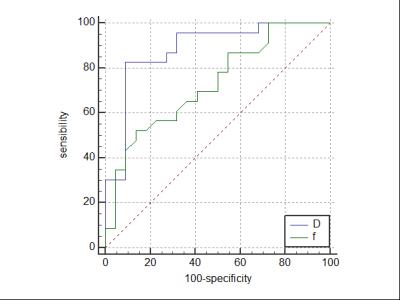
D and f values were significantly lower in malignant nodules(D=[0.79±0.19]×10-3mm2/s,[29.54±7.48]%) than in benign nodules (D=[1.20±0.34]×10-3mm2/s, [36.39±7.79]%),(Figure 1) while D* values showed no significant difference between malignant and benign nodules (D*=[11.21±2.31]×10-3mm2/s, D*=[10.53±2.77]×10-3mm2/s). According to ROC curve, D and f values showed diagnostic significance with the AUC values of 0.883, 0.729, respectively. The cutoff values for D and f were 0.874×10-3mm2/s (D values of benign nodules was greater than this value; accuracy rate 86.67%, sensitivity 82.61%, specificity 90.91%,PPV 90.47%, NPV83.34%), 28.50% (f values of benign nodules was greater than this value; accuracy rate68.89%,sensitivity52.17%,specificity86.36%,PPV79.99%, NPV63.34%),respectively(Figure 2).Discussion
Compared to regular DWI, iZoom DWI improved in the image quality in imaging of thyroid tumors. Based on the good image quality, IVIM exhibited its potential in the diagnosis of thyroid nodules. ROI of the whole lesion may also increase the stability of IVIM. The accuracy of US, which is common used in the clinical practice, in predicting malignant thyroid nodules showed a sensitivity from 26%to 87% and a specificity ranging from 40% to 93% from a recent meta-analysis. The D value of 0.874×10-3mm2/s for differentiating malignant and benign thyroid nodules yielded sensitivity and specificity of 82.61% and 90.91% in this study, which almost reached the upper limit of the accuracy based on US. More data will be involved in the further work. Analysis of the histogram of whole tumor will also be performed.Conclusion
IVIM parameters(D,f)derived from iZoom DWI measurements might help to differentiate malignant thyroid nodules from benign ones.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Erdem G, Erdem T, Muammer H, et al. Diffusion-weighted images differentiate benign from malignant thyroid nodules. J Magn Reson Imaging 2010;31:94–100.
2. Lu Y, Hatzoglou V, Banerjee S, et al. Repeatability investigation of reduced field-of-view diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging on thyroid glands. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2015;39:334–339.
3.Taviani V, Nagala S, Priest AN, McLean MA, Jani P, Graves MJ. 3T diffusion-weighted MRI of the thyroid gland with reduced distortion: preliminary results. Br J Radiol 2013;86:20130022
4. Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, AubinML, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 1988;168(2):497–505.
Figures