0818
Initial experience with magnetic resonance elastography and acoustic radiation force impulse elastography in renal transplant patients1Translational and Molecular Imaging Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States, 2Radiology, Groupe Hospitalier Pitié Salpêtrière, Paris, France, 3Recanati Miller Transplantation Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, United States
Synopsis
In this prospective study we compared renal transplant stiffness measured with MRE and ARFI ultrasound in 9 patients. Repeatability of both modalities was determined through test-retest imaging in 5 patients. MRE stiffness was significantly lower than ARFI stiffness as expected. MRE test-retest repeatability was excellent with mean coefficient of variation (CV) of 6%, while ARFI had CV of 30%. In addition, ARFI measurements exhibited a high inter-quartile range in the majority of cases suggesting inconsistency in the measurements. Our results suggest MRE is a more robust choice for renal transplant measurement compared to ARFI.
Purpose
To report initial results and repeatability of magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) and acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) ultrasound elastography in renal transplants.Methods
9 renal transplant patients (5F/4M, mean age 57y,) were enrolled in this IRB-approved prospective study. All patients had been transplanted more than 1 year before imaging, with 8 classified as stable (estimated MDRD serum eGFR 48-84 ml/min/1.73 m2) and 1 chronically dysfunctional (eGFR 24.6).
All patients underwent MRE examination at 1.5T (Aera) and ARFI examination using an Accuson S3000 system (both manufactured by Siemens) under fasting conditions. Renal allograft location was determined via a coronal HASTE sequence. MRE imaging was carried out in the coronal plane using a modified spin-echo EPI sequence (TR/TE 1500/49 ms, 10 slices, slice thickness 3 mm, FOV 400x400 mm2, matrix 128x128 interpolated to 256x256, voxel size 1.57x1.57x3.00 mm3, GRAPPA x2, 4 phase offsets, vibration frequency 60 Hz and wave motion was encoded in the slice-select direction, acquisition time 17 s). Wave images, elastograms and 95% confidence maps were automatically generated from a 2D multi-model direct inversion algorithm. ROIs were drawn offline using ImageJ software (NIH, Maryland, USA). Care was taken to ensure all measured areas were within the renal cortex and fell inside the 95% confidence map. ARFI measurements were acquired using an abdominal curved transducer (4C1) at 4 MHz. 10 measurements were acquired in the upper, middle and lower pole of the kidney by a trained radiologist and median wave speed (m/s) was calculated, as well as an estimate of shear stiffness.
Interquartile-range (IQR) and success rate (percentage of valid measurements obtained) were calculated for MRE and ARFI (with IQR <30% and success rate >60% considered a homogeneous ARFI measurement1. 5 patients underwent test-retest to assess repeatability of the modalities (with average delay of 24 days between examinations). MRE and ARFI stiffness measurement were compared using Mann-Whitney U tests. The relationship between the measurements was tested using Spearman correlation. Repeatability was assessed through coefficient of variation (CV) and Wilcoxon signed-rank tests.
Results
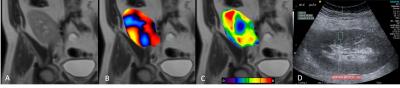
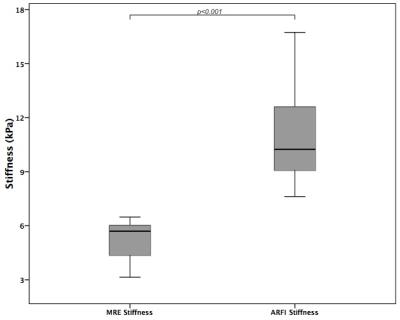
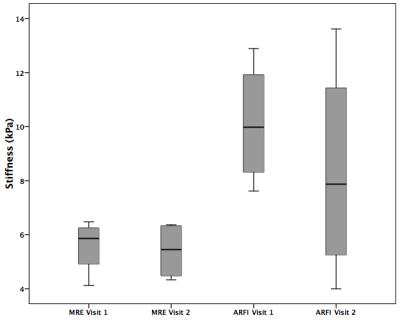
Example MRE wave images, elastograms and ARFI acquisitions are shown in Figure 1. One MRE examination (1/14; 7%) failed due to insufficient wave penetration to the kidney. MRE IQR was <30% in 11/13 (85%) measurements, while IQR of ARFI measurements was <30% in only 5/14 (36%) measurements. Success rate was >60% in all ARFI measurements. Renal stiffness measured by MRE was 5.25±1.1 kPa, which was significantly lower (p<0.001) than ARFI stiffness 11.00±2.74 kPa (Figure 2). ARFI and MRE measurements were not correlated (Spearman’s rho r=0.17, p>0.9). MRE showed excellent repeatability with a significantly lower (p<0.02) mean test-retest CV of 6% compared to 30% with ARFI (Figure 3). MRE reproducibility measurements were strongly correlated (Spearman’s rho r=1, p<0.01) compared to ARFI measurements which did not correlate (Spearman’s rho r=0.2, p>0.7).Discussion
ARFI stiffness was predicted to be higher than MRE stiffness due to the higher frequency mechanical waves generated during measurement2 which matched the data presented here. MRE measurements were completed with low failure rate and exhibited excellent repeatability, compared to ARFI. The ARFI measurements were acquired in a 1 cm x 0.5 cm FOV, with the probe held stationary between measurements. In this small FOV the IQR is required to be small (<30%) which signifies consistent measured values. In the data presented here this was not the case in the majority of measurements. The high success rate of the acquisitions but accompanying high IQR indicates that sufficient shear waves were produced during the ARFI measurements to produce a valid wave speed value; however the generated waves had varying speeds. MRE’s excellent repeatability has previously been reported in native kidneys3. ARFI repeatability has been previously reported in renal allografts4 and healthy and diseased native kidneys5 and poor inter and intra-observer agreement was reported. One factor which may influence ARFI repeatability in renal allograft measurements is the force applied to the transducer, which has been shown to affect the measured wave speed and the depth of measurement6. MRE results are less sensitive to operator influence and the ability to review wave propagation on the scanner console to ensure sufficient wave penetration is an additional benefit.Conclusion
MRE provides excellent repeatability and high success rate in renal transplant patients, compared to ARFI ultrasound indicating MRE may be a more robust choice for mechanical property estimation in renal transplants. Future work will assess the role of MRE in diagnosing renal transplant fibrosis and dysfunction.Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the MR technologists who assisted with the image acquisition and the clinical coordinators for recruitment assistance.References
1. Bota, S. et al. Factors that influence the correlation of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI), elastography with liver fibrosis. Med. Ultrason. 13, 135–140 (2011).
2. Ultrasound SWS Biomarker Ctte - QIBA Wiki. Available at: http://qibawiki.rsna.org/index.php/Ultrasound_SWS_Biomarker_Ctte. (Accessed: 28th October 2016)
3. Rouvière, O., Souchon, R., Pagnoux, G., Ménager, J.-M. & Chapelon, J.-Y. Magnetic resonance elastography of the kidneys: feasibility and reproducibility in young healthy adults. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging JMRI 34, 880–886 (2011).
4. Syversveen, T. et al. Assessment of renal allograft fibrosis by acoustic radiation force impulse quantification--a pilot study. Transpl. Int. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Organ Transplant. 24, 100–105 (2011). 5. Bruno, C. et al. Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) in the evaluation of the renal parenchymal stiffness in paediatric patients with vesicoureteral reflux: preliminary results. Eur. Radiol. 23, 3477–3484 (2013).
6. Syversveen, T. et al. Tissue elasticity estimated by acoustic radiation force impulse quantification depends on the applied transducer force: an experimental study in kidney transplant patients. Eur. Radiol. 22, 2130–2137 (2012).
Figures