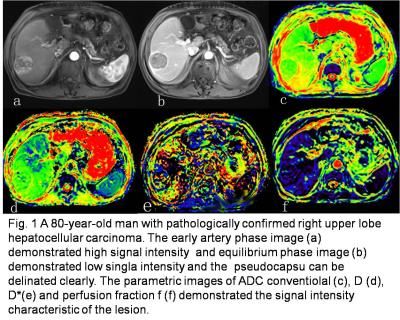
0665
Integrated slice-specific shimming (iShim) intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the liver: the value of differential diagnosis between benign and malignant hepatic tumors1Radiology Department, Binzhou Medical University Hospital, Binzhou, People's Republic of China, 2Emergency Department, Binzhou People's Hospital, Binzhou, People's Republic of China, 3Binzhou Medical University, Yantai, People's Republic of China, 4MR Scientific NE Asia, Siemens Healthcare, Beijing, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
This study investigated the value of ADC value, D, Dstar, ADC500~800 acquired with prototype iShim sequence at 3T. All those parameters demonstrated high diagnostic capacity in distinguishing benign and malignant hepatic lesions and in distinguishing different types of malignant hepatic lesions, among which ADC500~800 demonstrated the best diagnostic performance , which may have great value in clinical practice in future.
Backgrounds and Introduction
Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) imaging could allow separate estimation of microcirculation in the capillaries and in molecular diffusion. The pure diffusion characteristics (D), the perfusion characteristics (pseudodiffusion coefficient [Dstar]) and their proportion (perfusion fraction [f]) can be derived. But in vivo IVIM imaging studies in abdomen are hindered by variables that contribute to poor image quality and measurement reliability, e.g. distortion, susceptibility artifacts.
The prototype sequence iShim at the beginning acquires a 2D-field map for each EPI imaging slice. The field-map is used to determine the optimal center frequency and gradient offsets for the imaging slice. Center frequency and gradient offsets are then updated before the acquisition of each imaging slice in real time. This sequence integrated shimming (iShim) technique is an effective method which could reduce the susceptibility artifacts at 3T for diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and it also provide great potential for higher b-values imaging, which also been supported by the apparent improvement in signal integrity, spatial alignment [1].
The purpose of this study was to determine the value of iShim-DWI-derived IVIM parameters (D, Dstar, f), ADC500~800 and ADC value in differentiating benign and malignant hepatic tumors.
Materials and Methods
Sixty-six patients (37 men and 29 women, mean age 58.62±12.35 years, range: 34-80 years) which were confirmed by pathology, underwent MR imaging on a MAGNETOM Skyra 3T MR scanner (Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). All patients were divided into malignant group, which include 28 hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with 59 lesions, 9 cholangiocarcinoma patients, and 22 metastases patients, and benign group which include 20 hemangioma patients with 25lesions. The prototype iShim DWI sequence was included with parameters as follows: TR/ TE 5300 ms /56. 0 ms; matrix 160 x 117; voxel size 3.75 × 3.75 × 5.00 mm3; b values (0, 20, 40, 80, 120, 200, 500, 800, 1000) s/mm2. The IVIM parameters’ map (D, Dstar, f) and ADC map were generated by the post-processing algorithm affiliated in the prototype iShim sequence itself. The ADC500~800 map was calculated by using the images with b values (0, 500, 800,) s/mm2 on AW 4.3 workstation. All quantitative parameters measurements were performed by one radiologist (L.L., with 4 years of experience in abdomen MR imaging interpretation) on a high-resolution monitor on AW 4.3 workstation and were analyzed with one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction. For the diagnostic ability of those quantitative parameters, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was conducted to assess the cutoff values and diagnostic performance.Results
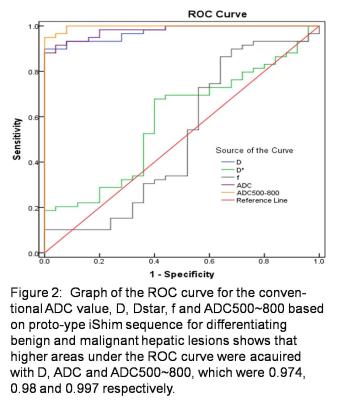
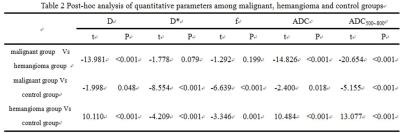
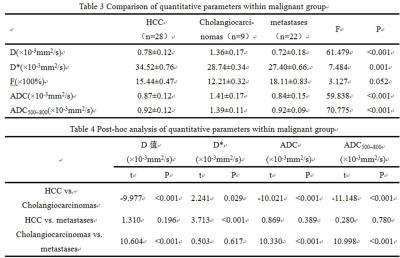
①The D, ADC and ADC500~800 of malignant group were significantly lower than that of benign group (P <0.05). The D, Dstar, f, ADC and ADC500~800 of the malignant group were significantly lower than that of the control group (P <0.05). The D, ADC and ADC500~800 of hemangioma group were significantly higher than that of the control group (P <0.05). The D * and f of hemangioma group were significantly lower than that of the control group (Table1, 2) . ② For malignant group, there were significant differences of D, Dstar, ADC and ADC500 ~ 800 among sub-groups of primary hepatocellular carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma and metastatic tumor. D, ADC, ADC500~800 of primary hepatocellular carcinoma was significantly lower than the sub-group of cholangiocarcinoma. Dstar of primary hepatocellular carcinoma was significantly higher than cholangiocarcinoma and metastatic tumor sub-group. The D, ADC and ADC500 ~ 800 of cholangiocarcinoma were significantly higher than that of metastatic tumor (Table3, 4). ③ In terms of the diagnostic performance of D, ADC and ADC500~800, area under the curve values were 0.974, 0.98 and 0.997 respectively (figure2).Discussion and Conclusion
Due to the decrease of susceptibility artifacts and image distortion, the accuracy of quantitative parameters including D, Dstar, f, ADC and ADC500~800 can be increased. In addition, the diaphragm navigation technology and continuous fat suppression during the whole breathing cycle that were implemented in this sequence improved the consistency of slice position among different b values. All those superiorities improved the accuracy of those quantitative parameters. The reasons for ADC500 ~ 800 and ADC having higher diagnostic efficiency are inferred as followings: (1) more b values were chosen to reduce fitting error; (2) the improvement of signal intensity for DWI images.
In conclusion, the parameters of conventional ADC value, D, Dstar, ADC500~800 acquired with prototype iShim sequence all have high diagnostic capacity in distinguishing benign and malignant hepatic lesions. Among these quantitative parameters, ADC500~800 demonstrated the best diagnostic performance in differential diagnosis between benign and malignant hepatic lesions, which may have great value in clinical practice in future.