0440
Free breathing T2* mapping of the Liver using a compressed sensing reconstruction1Radiology, AMC, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2Division of Imaging Sciences and Biomedical Engineering, King’s College London, London, United Kingdom, 3Medical Oncology, AMC, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 4Biomedical Engineering & Physics, AMC, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Synopsis
Hemochromatosis (iron overload) occurs in a range of liver diseaes.(1,2) Iron content can be measured invasively with liver biopsy but is commonly replaced by non-invasive MR measurements, including T2* mapping. This is commonly done in a breath-hold to reduce the effects of respiratory motion. In this work we show that a stack of stars radial golden angle T2* mapping multi echo sequence during free breathing in combination with CS reconstruction facilitates high resolution imaging in the liver. This approach bears promise beyond liver imaging for visualizing smaller organs and pathologies, e.g. the pancreas and lymph nodes.
Purpose
Hemochromatosis (iron overload) occurs in a range of liver diseaes.[1,2] Iron content can be measured invasively with liver biopsy but is commonly replaced by non-invasive MR measurements, including T2* mapping. This is commonly done in a breath-hold to reduce the effects of respiratory motion. Due to the breath-hold (short scan time) the spatial resolution is limited making it challenging to image smaller structures. In this work we propose a golden angle radial free-breathing T2* mapping combined with a compressed sensing (CS) reconstruction to make breath-holds redundant and ultimately allow for accurately imaging much smaller structures. This could be relevant in the context of therapy response in liver lesions such as after trans arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Some parts of the tumour may respond well and others not; high spatial resolution is required in patients not always able to hold their breath.Methods
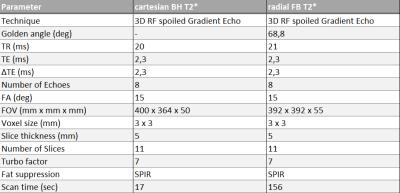
In total six healthy volunteers were scanned using a 3T (Ingenia; Philips, Best, Netherlands) MR scanner. Two multi echo (8 echoes) RF spoiled gradient echo were acquired, one in a single breath-hold echo using cartesian acquisition of k-space as well as a free breathing tiny golden angle radial k-space acquisition. The scan parameters are shown in figure 1. The radial acquisition facilitated a compressed sensing (CS) reconstruction with retrospective sorting of the data into different breathing motion states.
Post processing and reconstruction was done in MATLAB. Data were corrected for eddy currents and B0-phase delays.[3] An inverse Fourier transformation was performed in the kz stack direction. The k-space central points were 1D Fourier transformed for each slice to obtain a projection profile of the entire volume for each angle and followed by principal component analysis (PCA).[4] The respiratory motion was subsequently binned in 10 equally timed motion states (figure 1). The Berkeley Advanced Reconstruction Toolbox was used to perform a parallel-imaging CS reconstruction with a temporal total-variation l1-regularization constraint r=0.01, and 400 iterations.[5] Because of full sampling in the stack direction, the reconstruction could be performed in parallel for every slice. T2 star fitting was done with maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) method used for an unbiased estimation of mono-exponential T2 from magnitude images.
For the six volunteers the mean T2* value in the ROI, placed in the seventh segment of the liver carefully avoiding the veins, was determined using imageJ. Analysis of these values was performed in Graphpad and a Wilcoxon matched pairs test was performed to test if the two methods are significantly different. A p-value below 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
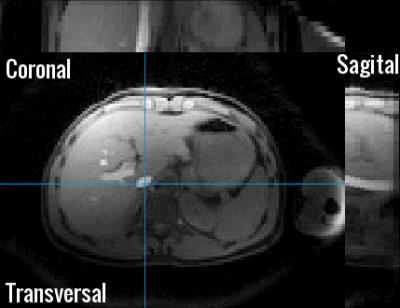
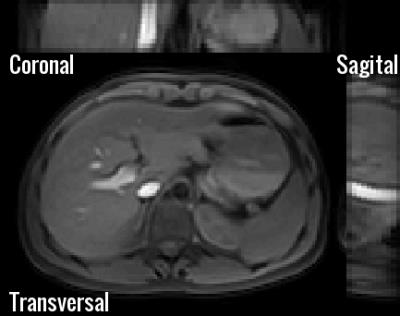
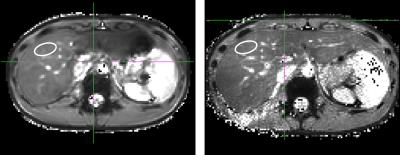
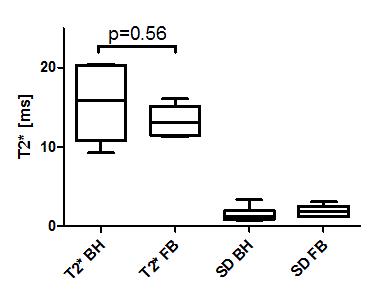
In Figure 2 and 3 the difference between the free breathing and breath-hold scan can be appreciated. In both figures the first echo is visualised. For the free breathing acquisition 10 motion breathing states reliably depict the respiratory motion in the abdomen. In Figure 4 T2* maps using a standard cartesian BH sequence (left) and the radial free-breathing CS reconstructed sequence (right) are shown. The free breathing T2* map shows more details in the liver; suggesting less susceptibility to motion. T2* values in the liver for the BH scan were 15.5 ± 4.7 ms while for the free breathing scans an average of 13.3 ± 2.1 ms was found. Figure 5 compares the mean T2* values for the two acquisitions showing no significant differences (p=0.56). The two right bars in figure 5 show the standard deviation within the ROI for the six volunteers.Discussion and Conclusion
We showed that T2*-maps in the liver can be acquired during free breathing and were qualitatively similar to T2*-maps obtained during breath-hold. Current work comprises further improvement of the spatial resolution of this technique. We anticipate that T2*-maps during free breathing suffer less from motion artefact that can easily hamper conventional breathhold scans.[6]
A stack of stars radial golden angle multi echo sequence during free breathing in combination with CS reconstruction facilitates high resolution imaging in the liver. This approach bears promise beyond liver imaging for visualizing smaller organs and pathologies, e.g. the pancreas and lymph nodes.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Runge JH, Akkerman EM, Troelstra MA, Nederveen AJ, Beuers U, Stoker J. Comparison of clinical MRI liver iron content measurements using signal intensity ratios, R 2 and R 2. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2016 Nov;41(11):2123-2131.
2. Sikorska K, Bernat A, Wroblewska A. Molecular pathogenesis and clinical consequences of iron overload in liver cirrhosis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2016 Oct;15(5):461-479.
3. Moussavi, Amir, et al. "Correction of gradient-induced phase errors in radial MRI." Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 71.1 (2014): 308-312.
4. Feng L, Axel L, Chandarana H, Block KT, Sodickson DK, Otazo R. XD-GRASP: Golden-angle radial MRI with reconstruction of extra motion-state dimensions using compressed sensing. Magn Reson Med. 2016 Feb;75(2):775-88. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25665. Epub 2015 Mar 25.
5. BART: version 0.3.01 (2016) DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.
6. Lens E, Gurney-Champion OJ, Tekelenburg DR, van Kesteren Z, Parkes MJ, van Tienhoven G, Nederveen AJ, van der Horst A, Bel A. Abdominal organ motion during inhalation and exhalation breath-holds: pancreatic motion at different lung volumes compared. Radiother Oncol. 2016 Oct 20. pii: S0167-8140(16)34334-1. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2016.09.012.
Figures