0236
Prediction of treatment response using baseline structural and functional MRI in first-episode antipsychotic-naive schizophreniaSu Lui1, Lu Liu2, Yuan Xiao2, Bo Tao2, Biqiu Tang2, and Qiyong Gong2
1west china hospital of sichuan university, chengdu, People's Republic of China, 2west china hospital of sichuan university
Synopsis
Finding imaging biomarkers which could predict the treatment response is quite important to help the selection of therapy and save health resource.
Clinical Question
Up to now, there is no way to predict the treatment response for first-episode antipsychotic-naive schizophrenia, which is a big challenge for psychiatrists.Impact
Nearly 1/3 schizophrenia patients are not response to the antipsychotics treatment(1). However, there is no way by now to separate the no-responders from the responders before treatment, which cause a big challenge for any psychiatrist. Finding imaging biomarkers which could predict the treatment response is quite important to help the selection of therapy and save health resource.Approach
Multi-modal MRI including high resolution T1 weighted image and resting state functional MRI were acquired from 70 drug-naive schizophrenia patients and 70 healthy controls at baseline. Severity of symptoms in patients were assessed by Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) both at baseline and after 1 years' treatment. Responder group was defined as patients with the reduction ratio of PANSS scores between baseline and that after 1 years' treatment more than 50%(2). Finally, there were 45 responders and 25 non-responders. Gray matter anatomical indexes including cortical thickness (CT), volume, cortical surface areas and functional parameters including amplitude of low frequency fluctuation (ALFF) and regional homogeneity (ReHo) were used for the machine learning analysis using support vector machine (SVM).Gains and Losses
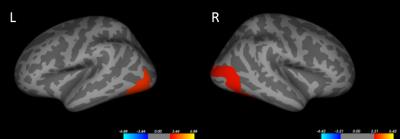
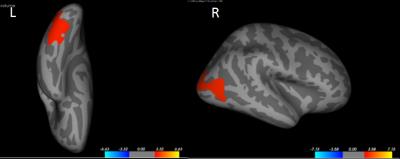
Compared with the non-responder group, the responder group had increased volume in bilateral lateral occipital gyrus, right posterior cingulate gyrus, right precentral gyrus and right rostral middle frontal gyrus(Figure 2). In addition the responder group have increased surface areas in bilateral lateral occipital gyrus(Figure 1). And these changes are different between schizophrenia patients and healthy controls. However, there are no significant difference of ALFF and ReHo between two patient groups. Furthermore, SVM allowed the classification of the two groups with diagnostic accuracy of gray matter volume that was 77.5% (sensitivity=70%, and specificity=85%, P≤0.001), however, the accuracy of ALFF and ReHo was so low and it had no stastistically significant differences. These results provide evidence that the structural MRI instead of the functional MRI could be used to predict the treatment response of schizophrenia. However, not all of the schizophrenia patients received single drug therapy, and these findings should be verified in another lager sample of first-episode antipsychotic-naive schizophrenia.Preliminary Data
Previous studies are mainly included one imaging approach, in our recent study, we used multi-modal MRI approach, which can provide more information and help to further understanding of schizophrenia.Acknowledgements
This research was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation(Grant Nos. 81222018, 81371527), National Youth Top-notch Talent Support Program of China and Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (PCSIRT, Grant No. IRT 1272) of China.References
1. Lindenmayer JP. Treatment refractory schizophrenia. Psychiatr Q. 2000;71:373–384.
2. Leucht S, Davis J.M., Engel R.R. et al. Definitions of response and remission in schizophrenia: recommendations for their use and their presentation. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 2009;(438):7-14.