0151
Investigation of zero TE ASL MRA in the follow-up after endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysm at 1.5T1Beijing Hospital, Beijing, People's Republic of China
Synopsis
It is necessary to follow up the intracranial aneurysms treated with coil or/and stent for recanalization or remnant. TOF MRA, though performed well, is susceptible to metallic artifact and flow artifact. ASL MRA with zero TE acquisition has potential advantages. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the performance of ASL MRA by comparing with TOF MRA, using DSA as gold standard. It was demonstrated that ASL MRA featured significantly better consistency with DSA for aneurysm remnant diagnosis and led to superior image quality in the presence of intra-stent lumen as compared to TOF at 1.5T.
Purpose
Endovascular embolization with coils is now a commonly performed treatment for intracranial aneurysms. However, there is a reported 20~30% risk of aneurysm recanalization1, which necessitates the need of follow-up examinations to evaluate the aneurysm occlusion. TOF imaging has been shown to perform well in evaluating coiled aneurysms, however is susceptible to metallic artifacts by stent, and the hemodynamic abnormality may lead to signal voids in aneurysms2. Contrast enhanced MRA may overcome the shortcomings of TOF but requires external contrast and moreover the residual contrast in aneurysm may lead to misdiagnosis. ASL MRA with zTE acquisition has potential advantages of CE MRA without its shortcomings. Its use on aneurysms has been rarely reported, especially on 1.5T. In this study, we compare the use of zTE MRA to TOF in the assessment of intracranial aneurysm at 1.5T, using DSA as gold standard.
Methods
A total of 24 patients with 27 aneurysms that underwent coil embolization with or without stent were enrolled in this study, informed consent forms were obtained. Both TOF and zTE MRA3 were performed on a 1.5T whole body scanner (MR360, GE,USA) equipped with an 8 channel head coil, and DSA was performed within one week of the MR exams. Parameters for 3D TOF: 3D SPGR, TR/TE=5/2ms, FA=20, slice = 1.4mm, 32 slices and 3 slabs. Parameters for zTE MRA: TR/TE = 0.5/0ms, FA=5, 1mm isotropic, The MR image assessments were performed by two experienced radiologists and the DSA image was assessed by one interventional neurologist. A 2-point system was used to assess if there is recanalization: 1 for with and 2 for without recanalization. Fisher test and Kappa coefficient was used to determine the consistency between the TOF and DSA, between ASL MRA and DSA respectively. The visualization of stented aneurysms was also assessed with 4-point scale: 1 for totally invisible of the intra-stent lumen, 2 for invisible even though there is some signal, 3 for visible with a little artifact within the stent, 4 for clearly visible with excellent image quality.Results
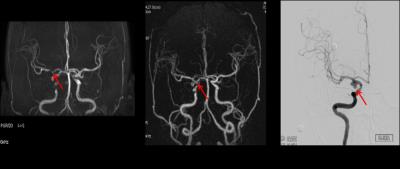
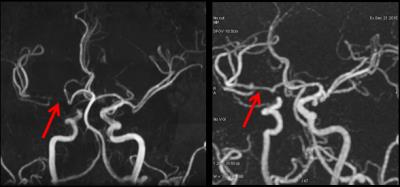
A typical set of DSA, TOF and zTE MRA images of a patient with remnant are shown in Fig. 1, and the readings of different images of the cohort are summarized in Table 1. It was seen that DSA detected 13 cases of remnant, and zTE MRA led to a detection rate closer to that of DSA as compared to TOF. The Kappa value for TOF and ASL MRA with respect to DSA are 0.702 and 0.852 respectively. As to the visualization of intra-stent lumen (Fig. 2), there were 11 cases with TOF MRA whose the intra-stent lumen was invisible due to artifacts, whereas there were only two cases with zTE MRA. There was statistical significance in the scoring results of the intra-stent lumen visibility.Discussion and conclusion
MR angiography is able to provide good complementary information to the following up of the coil embolized intracranial aneurysms, and may be a substitute to the current gold standard DSA. TOF MRA itself has intrinsic limitations in imaging coiled aneurysms. Zero TE ASL MRA features the advantages of contrast enhanced MRA while being contrast free. In this study, it was demonstrated that ASL MRA featured significantly better consistency with DSA for aneurysm remnant diagnosis as compared to TOF, and led to superior image quality in the presence of intra-stent lumen as compared to TOF at 1.5T, which is already less sensitive to the susceptibility artifacts as compared to 3T.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Piotin, M, et al. Radiology,2007, 243:500–508.
2. Cho, WS, et al. ActaRadiol 2014,55:604–13.
3. R. Irie, et al. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol,2015.
Figures