0145
4D MR Angiography with Pseudo-Continuous Arterial Spin Labelling Combined with CENTRA-Keyhole (4D-PACK): Visualization of Distal Cerebral Arteries in Moyamoya Disease1Clinical Radiology, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan, 2Philips Electronics Japan, Tokyo, Japan
Synopsis
In the present study, we demonstrated the clinical utility of 4D-MR angiography with pCASL combined with CENTRA-keyhole (4D-PACK) in Moyamoya disease by comparing with a well-established pulsed ASL-based 4D-MRA called contrast inherent inflow enhanced multi-phase angiography (CINEMA). 4D-PACK provided higher CNRs than CINEMA in distal MCA branches in later phases indicating that 4D-PACK enables better visualizations of distal cerebral arteries supplied by collaterals vessels during a long transit time. This could be due to higher flow signal obtained with pCASL and less saturation effect after labeling. 4D-PACK can be a non-invasive clinical tool in assessing hemodynamics in Moyamoya disease.
Purpose
Moyamoya disease is a cerebrovascular steno-occlusive disorder which is defined as progressive steno-occlusion of cerebral vasculature with particular involvement of the terminal internal carotid artery1. The leptomeningeal anastomosis (LMA) collaterals play an important role in maintaining cerebral perfusion in this disease2. Evaluations of distal cerebral arteries and dynamic flow information are important especially in decisions of surgical intervention in patients. Arterial spin labeling (ASL) has its capacity for non-contrast enhanced intracranial 4D-MR angiography (MRA)3-7. The challenge in a ASL-based 4D-MRA is to acquire multi-phase data within a clinically acceptable scan time while keeping a high flow signal. The vessel signal in ASL depends on the transit time from the labeling to the targeted regions. If the transit time is longer than the order of the blood T1, the vessel visualization will be reduced. Thus, these methods could be of limited usefulness in Moyamoya disease, in which transit time could be very long. Pseudo-continuous ASL (pCASL)-based 4D-MRA can provide high flow signal, but scan time prolongation is a problem to be solved. Recently we proposed a novel approach named 4D-pCASL-based angiography using CENTRA-keyhole (4D-PACK) for intracranial dynamic MRA8. This method overcomes the aforementioned issues and enables multi-phase acquisition within a short scan time while keeping a high flow signal in later phases. In this study, we evaluated the utility of 4D-PACK in the visualization of distal cerebral arteries and LMA collaterals in Moyamoya disease by comparing with a well-established pulsed ASL-based 4D-MRA called contrast inherent inflow enhanced multi-phase angiography (CINEMA).Methods
[Patients] Thirteen patients with Moyamoya disease (age 29.4 ± 18.1 year-old; 4 males, 9 females) were examined. Twenty-one out of 26 cerebral hemispheres that did not receive bypass surgeries were analyzed. All patients underwent both MRA and digital subtraction angiography (DSA) within an interval of 3 months.
[MRI] Both CINEMA and 4D-PACK images were obtained on a 3T MR scanner (Ingenia 3.0CX, Philips).
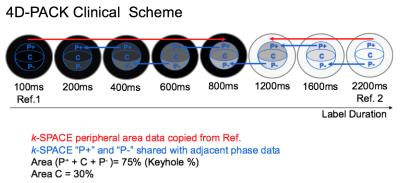
4D-PACK: Images were obtained by changing the label duration: 100ms, 200ms, 400ms, 600ms, 800ms, 1200ms, 1600ms, 2200ms. Each phase session consists of label and control imaging. The 4D-PACK clinical scheme is described in Figure 1. The first phase (100ms) data was used as a reference in the first five (100-800ms) and the last phase data (2200ms) was used in the last three phases (1200-2200ms) with keyhole 75%. In addition, echo data were shard with adjacent phase data with view sharing technique. The other parameters were: sequence, 3D T1-TFE; TR/TE, 4.9/1.73msec; FA, 11°; ETL, 60; 3D slab thickness, 80mm; voxel size, 1.0*1.4*1.6; SENSE factor, 3.0; acquisition time: 6min5sec.
CINEMA: Multi-phase images were obtained by look-locker readout after the labeling by pulsed ASL. The post labeling delay ranged from 200ms to 2200ms at an interval of 200ms. The spatial resolution and imaging geometry was identical to those in 4D-PACK. The acquisition time was 4min59s.
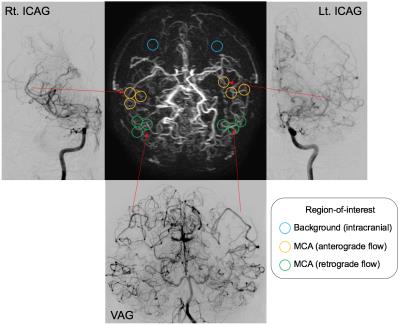
[Image Analysis] The maximum contrast-to-noise ratios (CNRs) were measured in distal middle cerebral artery (MCA) branches (M3-4) with anterograde flow or retrograde flow via LMA collaterals on both MRAs with reference to the DSA findings (Figure 2) with the following equation; CNR = (Vesselmax – WMave) / WMSD. [Statistical Analysis] CNRs in distal MCA branches were compared between CINEMA and 4D-PACK at each time point by Student’s t-test. CNRs were also compared between anterograde and retrograde flow.
Results
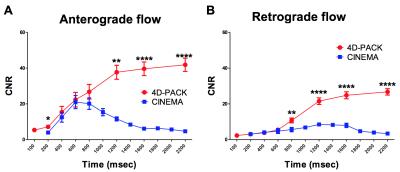
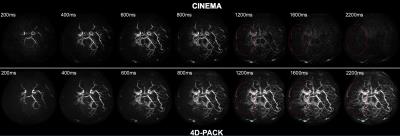
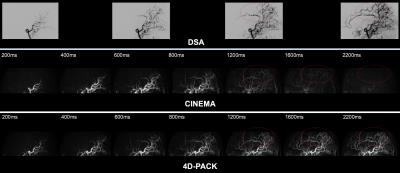
Figure 3 shows temporal changes in CNR of anterograde and retrograde flow signals in distal MCA branches. The CNR of anterograde flow signal was significantly higher in 4D-PACK than in CINEMA at phases of 200ms (P<0.05), 1200ms (P<0.01), 1600ms (P<0.0001), and 2200ms (P<0.0001). The CNR of retrograde flow signal was significantly higher in 4D-PACK than in CINEMA at phase of 800ms (P<0.01), 1200ms (P<0.0001), 1600ms (P<0.0001), and 2200ms (P<0.0001). Figure 4 shows that the anterograde flow via Moyamoya vessels is well visualized in 4D-PACK in later phases (1200-2200ms) while CINEA fails to depict these vessels. Figure 5 shows that the retrograde flow via LMA is well visualized in 4D-PACK in later phases (1200-2200ms) compared with CINEMA.Discussion
We found that 4D-PACK provided higher CNRs than CINEMA in distal MCA branches in later phases. This could be due to higher flow signal obtained with pCASL and less saturation effect after labeling. The results indicate that 4D-PACK enables better visualization of distal cerebral arteries supplied by collaterals vessels during a long transit time.
Conclusion
4D-PACK was able to visualize distal cerebral arteries and collateral flow in Moyamoya disease. 4D-PACK could be a non-invasive clinical tool in assessing hemodynamics in this disease.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Suzuki J, Takaku A. Cerebrovascular "moyamoya" disease. Disease showing abnormal net-like vessels in base of brain. Archives of neurology. 1969;20(3):288-99.
2. Togao O, Mihara F, Yoshiura T, et al. Cerebral hemodynamics in Moyamoya disease: correlation between perfusion-weighted MR imaging and cerebral angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006;27(2):391-7.
3. Yu S, Yan L, Yao Y, Wang S, Yang M, Wang B, Zhuo Y, Ai L, Miao X, Zhao J, Wang DJ. Noncontrast dynamic MRA in intracranial arteriovenous malformation (AVM), comparison with time of flight (TOF) and digital subtraction angiography (DSA). Magn Reson Imaging 2012;30:869.
4. Yan L, Wang S, Zhuo Y, Wolf RL, Stiefel MF, An J, Ye Y, Zhang Q, Melhem ER, Wang DJ,. Unenhanced dynamic MR angiography: high spatial and temporal resolution by using true fisp-based spin tagging with alternating radiofrequency. Radiology 2010;256:270.
5. Wu H, Block WF, Turski PA, Mistretta CA, Rusinak DJ, Wu Y, Johnson KM. Noncontrast dynamic 3D intracranial MR angiography using pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling (pCASL) and accelerated 3D radial acquisition. J Magn Reson Imaging 2014;39:1320.
6. Robson PM, Dai W, Shankaranarayanan A, Rofsky NM, Alsop DC,. Time-resolved vessel-selective digital subtraction MR angiography of the cerebral vasculature with arterial spin labeling. Radiology 2010;257:507.
7. Iryo Y, Hirai T, Kai Y, Nakamura M, Shigematsu Y, Kitajima M, Azuma M, Komi M, Morita K, Yamashita Y. Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas: evaluation with 3-T four-dimensional MR angiography using arterial spin labeling. Radiology. 2014 Apr;271(1):193-9.
8. Obara M, Togao O, Okuaki T, et al. Non-contrast enhanced 4D intracranial MR angiography based on pseudo-continuous arterial spin labelling (pCASL) with the keyhole technique. Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 24 (2016) 4376
Figures