0088
Improved Muscle Microstructure Analysis with Diffusion Weighted Imaging and Advanced Tissue Modeling1Waisman Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States, 2Radiology, University of Wisconsin-Madison
Synopsis
Studies on musculoskeletal systems can benefit by quantitative mapping of the tissue microstructure. Parameters from traditional diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) may serve as bio-markers for assessing muscle fiber health. While these parameters are sensitive to changes of muscle fiber orientation, length and tension, they are non-specific to the changes of microstructure and microcomposition of muscle fibers. In this study, we proposed to use multi-shell diffusion weighted imaging acquisition with advanced diffusion and micro tissue modeling to improve in-vivo muscle fiber analysis and demonstrated the feasibility of applying these methods on in-vivo human thigh muscle imaging.
Purpose
Quantitative diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) have recently been used in muscle imaging to assess muscle degeneration such as duchenne muscular dystrophy and functional changes such as intense fatigue and muscle injury1-3. Traditional DWI and DTI parameters including mean diffusion (MD), fractional anisotropy (FA) and diffusion eigen values demonstrated great sensitivity to the changes of the muscle conditions. However, those traditional parameters are non-specific to tissue structure and are limited in offering information under complex fiber environment, i.e. crossing-fibers4. To overcome the limitations of current diffusion methods, we proposed to incorporate advanced tissue modeling with extended diffusion acquisition to improve the analysis specificity regarding tissue microstructure and microenvironment in the muscle. In this study, we conducted a pilot study to demonstrate the feasibility of applying the higher angular resolution diffusion imaging5 (HARDI) and neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging (NODDI)6 tissue modeling on the thigh muscle and comparing the results with regular DWI and DTI.Methods
Image Acquisition: An in-vivo imaging experiment was performed for the right thigh of one young healthy subject in 3T MR750 (GE Healthcare, Waukesha USA) using a 32-channel wrap coil. An axially acquired $$$T_1$$$-weighted sequence was acquired for assessment of anatomy with the imaging parameters as TR/TE=750/16 ms, 15 cm field of view, 256 x 256 matrix, 3 mm slice thickness. The multi-shell diffusion weighted sequence was acquired using diffusion-weighted single shot echo planer imaging with 6 b=0, 9 b=500 s$$$\cdot$$$mm$$$^{-2}$$$, 18 b=800 s$$$\cdot$$$mm$$$^{-2}$$$ and 36 b=2000 s$$$\cdot$$$mm$$$^{-2}$$$ diffusion weighting in uniformly distributed directions on a unit sphere. Imaging parameters include TR/TE 8575/55 ms, 15 cm field of view, 64 $$$\times$$$ 64 matrix size, 3 mm slice thickness and 69 slices. Image Analysis: The correction for motion and eddy current distortion was applied by using the eddy tool from FSL7. Several different diffusion models were estimated using the corrected DWI data. [1] MD and FA were estimated using Camino with traditional DTI model8. [2] High-resolution (0.25 mm$$$^3$$$ isotropic) muscle fiber density images9,10 was generated using over 5 million muscle fibers generated using streamline tractography on the fiber orientation distribution functions (FOD) estimated by constrained spherical deconvolution11,12 with multi-shell response functions13. The response functions were estimated directly from the corrected DWI data14 thus avoiding a necessity for a co-registered $$$T_1$$$-weighted image. Minimizing cross-modality image registrations when possible reduces confounding factors in image analysis. [3] NODDI model was fit to the corrected DWI data to assess the fiber orientation dispersion and density imaging.Results
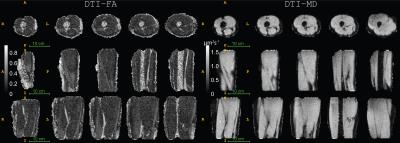
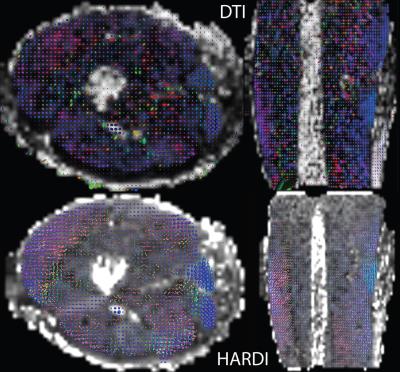
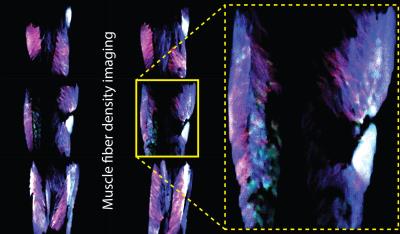
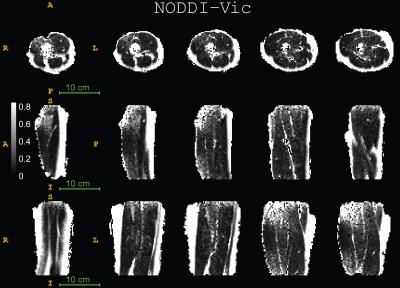
Fig. 1 displays the DTI measures: FA - fractional anisotropy and MD - mean diffusion for the whole thigh muscle group and Fig. 2 shows some of the reconstructed muscle fiber pathways from DTI which can be used in estimating muscle length, orientation and stress strength. Fig. 3 shows the estimated diffusion tensors (top) obtained from DTI in contrast to the FODs (bottom) obtained from HARDI in axial and coronal views of the thigh muscles. There is clearly more information in FODs for complex muscle fiber crossing orientations which cannot be resolved using DTI. Fig. 4 shows coronal slices of the high-resolution muscle fiber density maps obtained using FODs which can be used to assess micro-fiber changes or damages. Fig. 5 shows the intra-cellular volume fraction (Vic) parameter from the estimated NODDI model which can be useful to assess muscle microcomposition changes caused by tissue degeneration such as muscle dystrophy and inflammation.Discussion and Conclusion
We demonstrated the feasibility of implementing advanced diffusion weighted imaging and tissue modeling techniques in skeletal muscle imaging. We observed that the FODs reveal complex fiber orientation within the thigh and performing spherical deconvolution can be beneficial since the traditional diffusion tensors do not capture the multiple peak orientations needed to reconstruct the muscle fibers accurately. The muscle fiber density imaging can be used to derive microstructural contrast at much higher resolution than the acquisition resolution which can potentially benefit detection of micro-fiber tears due to injury. Both DTI maps and NODDI maps provide good tissue contrast and the intra-cellular volume fraction from NODDI might offer different tissue contrast with regards to the fiber microcomposition and microstructure. The other parameters in the NODDI model such as the orientation dispersion and free water fraction provided limited tissue contrast in the thigh. The result from current pilot study clearly shows promising evidence that the advanced diffusion tissue models can benefit investigations in musculoskeletal systems. However, the applicability, reproducibility and reliability of these advanced diffusion tissue models in MSK imaging still remain a challenging research topic and need future studies.Acknowledgements
We acknowledge support from NIH R01-AR068373, R01-EB02883, UL1RR025011, P30-HD003352.References
1. Hooijmans MT, Damon BM, Froeling M, Versluis MJ, Burakiewicz J, Verschuuren JJ, Niks EH, Webb AG, Kan HE. Evaluation of skeletal muscle DTI in patients with duchenne muscular dystrophy. NMR Biomed 2015;28(11):1589-1597.
2. Li GD, Liang YY, Xu P, Ling J, Chen YM. Diffusion-Tensor Imaging of Thigh Muscles in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Correlation of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Fractional Anisotropy Values With Fatty Infiltration. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2016;206(4):867-870.
3. Ai T, Yu K, Gao L, Zhang P, Goerner F, Runge VM, Li X. Diffusion tensor imaging in evaluation of thigh muscles in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Br J Radiol 2014;87(1043):20140261.
4. Farquharson, S., Tournier, J. D., Calamante, F., Fabinyi, G., Schneider-Kolsky, M., Jackson, G. D., & Connelly, A. (2013). White matter fiber tractography: why we need to move beyond DTI: clinical article. Journal of neurosurgery, 118(6), 1367-1377.
5. Tuch DS, Reese TG, Wiegell MR, et al. (2002). "High angular resolution diffusion imaging reveals intravoxel white matter fiber heterogeneity". Magn. Res. Med. 48 (4): 577–582.
6. Zhang, H., Schneider, T., Wheeler-Kingshott, C. A., & Alexander, D. C. (2012). NODDI: practical in vivo neurite orientation dispersion and density imaging of the human brain. Neuroimage, 61(4), 1000-1016.
7. Jesper L. R. Andersson and Stamatios N. Sotiropoulos. An integrated approach to correction for off-resonance effects and subject movement in diffusion MR imaging. NeuroImage, 125:1063-1078, 2016.
8. Cook, P. A., Bai, Y., Nedjati-Gilani, S. K. K. S., Seunarine, K. K., Hall, M. G., Parker, G. J., & Alexander, D. C. (2006, May). Camino: open-source diffusion-MRI reconstruction and processing. In 14th scientific meeting of the international society for magnetic resonance in medicine (Vol. 2759). Seattle WA, USA.
9. Calamante, F., Tournier, J. D., Jackson, G. D., & Connelly, A. (2010). Track-density imaging (TDI): super-resolution white matter imaging using whole-brain track-density mapping. Neuroimage, 53(4), 1233-1243.
10. Ellingson, B. M., Salamon, N., Woodworth, D. C., & Holly, L. T. (2015). Correlation between degree of subvoxel spinal cord compression measured with super-resolution tract density imaging and neurological impairment in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine, 22(6), 631-638.
11. Tournier, J. D., Calamante, F., & Connelly, A. (2007). Robust determination of the fibre orientation distribution in diffusion MRI: non-negativity constrained super-resolved spherical deconvolution. NeuroImage, 35(4), 1459-1472.
12. Tournier, J. D., Yeh, C. H., Calamante, F., Cho, K. H., Connelly, A., & Lin, C. P. (2008). Resolving crossing fibres using constrained spherical deconvolution: validation using diffusion-weighted imaging phantom data. Neuroimage, 42(2), 617-625.
13. Jeurissen, B., Tournier, J. D., Dhollander, T., Connelly, A., & Sijbers, J. (2014). Multi-tissue constrained spherical deconvolution for improved analysis of multi-shell diffusion MRI data. NeuroImage, 103, 411-426.
14. Dhollander, T., Raffelt, D., Connelly, A. (2016). Unsupervised 3-tissue response function estimation from single-shell or multi-shell diffusion MR data without a co-registered T1 image. ISMRM Workshop on Breaking the Barriers of Diffusion MRI. pp. 5
Figures