4686
Implications of within-scan patient head motion on B1+ homogeneity and Specific Absorption Rate at 7T1CUBRIC, School of Psychology, Cardiff University, Cardiff, United Kingdom, 2Center for Magnetic Resonance Research, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States, 3Department of Radiology, School of Medicine, New York University, New York, NY, United States
Synopsis
Parallel-transmit pulses are commonly used to improve B1+-homogeneity at higher field strengths, while local-SAR constraints are applied to ensure safety. However, patient motion may become unavoidable with longer scans or less cooperative patients, and motion may affect B1+-homogeneity and local-SAR. We investigated the effect of all 6 degrees-of-freedom of head motion on B1+-homogeneity and local-SAR for parallel-transmit multi-spoke pulses using simulations. We observed more than a 2-fold increase in local-SAR due to motion for some pulses. We also investigated the changes in B1+-homogeneity of spokes pulses using in-vivo B1+-maps and showed regional variations between 12%-22% in the excitation profile.
Introduction
The use of multi-channel parallel-transmit (pTx) arrays has been commonly investigated to improve B1+-homogeneity at higher field strengths (7T). However, the possibility of creating local-SAR/local-temperature hotspots due to constructive interference of the electric field has raised questions on safety. Thus, local-SAR/local-temperature has been used as a safety constraint in pulse design, and several safety margins have been applied in practice to account for modelling imperfections1-10. However, the effect of patient motion on B1+-homogeneity and safety remains as an important question that has received little attention. Patient motion might become unavoidable especially with longer scans or less cooperative patients, such as in pediatric imaging11-14, or for patients with Parkinson’s15 or dementia16.
Earlier studies have investigated the effect of body position on B1+-homogeneity and local-SAR17-20. However, these studies have been limited to a subset of motion types and have focussed on the initial positioning of the patient rather than motion during the scan. In this study, we investigate, using simulation, the effect of all 6 degrees-of-freedom head motion during scan on B1+-homogeneity and local-SAR for multi-spoke pulses. Moreover, we show the effect of head motion on excitation profiles at 7T using in-vivo B1+-maps of an 8-channel pTx coil.
Methods
Simulations were conducted using Sim4Life (ZMT, Zurich, Switzerland) for an 8-channel loop array and the body model Ella (IT’IS, Zurich, Switzerland). Patient motion was modelled by keeping the body model stationary and moving the RF array. This approach i) prevents changes in electromagnetic properties of the model due to voxelization effects as it keeps the tissues in the body model intact, ii) isolates the B1+-related effects as no image-registration is required. The array was i) displaced along or rotated around the three main axis, and ii) displaced along two-dimensions on coronal and axial planes for a total of 105 positions. Displacements and rotations of 1/2/5/10/15/20 mm or degrees were simulated, unless the prescribed motion would overlap the coil and the body model. Adaptive voxelization was used with maximum voxel size of 2mm for the model and <40% of conductor width for the array. Coil elements were checked for connectivity and voxelization prior to simulation.
For six different axial slices (each separated by 18mm), 1-spoke, 2-spoke, 3-spoke RF excitation pulses were designed to optimize for in-slice B1+-homogeneity21. Normalized root-mean-squared error (nRMSE) was calculated on the complex excitation profiles since phase changes also contribute to error due to motion in practice. 1-gram averaged maximum local-SAR was calculated for each relative position of the model and normalized by the maximum local-SAR for the case without motion.
In vivo experiments were conducted on a 7T scanner (Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany) with an 8-/32-channel pTx/Rx coil (Nova Medical, MA, USA). The participant moved his head between scans while B1+-maps and GRE images were acquired. Images were registered using masks created from the GRE images and head motion was estimated to be Right/Anterior/Yaw: -2.6mm/7.5mm/0degree (position2), 5.6mm/15.5mm/1.6degree (position3), 5.4mm/0.4mm/0.9degree (position4). 1-spoke, 2-spoke, 3-spoke pulses were designed using the B1+-maps acquired in the first position. Using the in-vivo B1+-maps acquired at different positions, the excitation profiles of the designed pulses were simulated. The difference between the excitation profiles due to participant motion were analysed.
Results
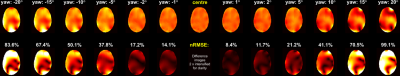
Figure 1 shows the variation of nRMSE for a 3-spoke pulse designed for imaging the temporal lobe. The excitation profile was more sensitive to in-slice motion (right-left, anterior-posterior, yaw). Figure 2 demonstrates the change in the profile as the body model rotates in yaw. Figure 3 shows that, while the inner-slices are more sensitive to in-(axial-)slice motion, the outer slices (cerebellum/crown) are more susceptible to superior-inferior, roll and pitch motion.
Figure 4 shows the change in the maximum local-SAR observed for all 18 pulses. In 3% of the cases, the maximum local-SAR increased by more than 50% compared to the respective maximum local-SAR at the centre position and increased by more than 2-fold in ten cases. For one slice/pulse combination, local-SAR increased with a slope of 6.5%-per-mm of lateral motion.
Figure 5 shows the changes in the excitation profiles simulated using in-vivo B1+-maps. The head motion caused 12%-22% change in the excitation profiles.
Discussion
We have demonstrated that the B1+-homogeneity created via multi-spoke pTx pulses is highly susceptible to within-scan patient motion. This is especially important for patient populations that may not stay still for extended durations11-16. More importantly, the results showed that maximum local-SAR does not have a straightforward dependence only on the amount of motion and it is also highly sensitive to the slice/pulse combination. Finally, the range of increase in maximum local-SAR due to motion is similar to previous literature, although we observed the maximum increase for lateral displacement which was excluded in Refs17-20.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Cloos MA, Luong M, Ferrand G, Amadon A, Le Bihan D, Boulant N. Local SAR reduction in parallel excitation based on channel-dependent Tikhonov parameters. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2010;32(5):1209-1216.
2. Lee J, Gebhardt M, Wald LL, Adalsteinsson E. Local SAR in parallel transmission pulse design. Magn Reson Med 2012;67(6):1566-1578.
3. Wu X, Schmitter S, Auerbach EJ, Moeller S, Ugurbil K, Van de Moortele PF. Simultaneous multislice multiband parallel radiofrequency excitation with independent slice-specific transmit B1 homogenization. Magn Reson Med 2013;70(3):630-638.
4. Guerin B, Setsompop K, Ye H, Poser BA, Stenger AV, Wald LL. Design of parallel transmission pulses for simultaneous multislice with explicit control for peak power and local specific absorption rate. Magn Reson Med 2015;73(5):1946-1953.
5. Guerin B, Gebhardt M, Serano P, Adalsteinsson E, Hamm M, Pfeuffer J, Nistler J, Wald LL. Comparison of simulated parallel transmit body arrays at 3 T using excitation uniformity, global SAR, local SAR, and power efficiency metrics. Magn Reson Med 2015;73(3):1137-1150.
6. Deniz CM, Carluccio G, Sodickson DK, Collins CM. Non-Iterative Parallel Transmission RF Pulse Design with Strict Temperature Constraints. 2015; Toronto, Canada. p 549.
7. Wu X, Schmitter S, Auerbach EJ, Ugurbil K, Van de Moortele PF. A generalized slab-wise framework for parallel transmit multiband RF pulse design. Magn Reson Med 2016;75(4):1444-1456.
8. Vinding MS, Guerin B, Vosegaard T, Nielsen NC. Local SAR, global SAR, and power-constrained large-flip-angle pulses with optimal control and virtual observation points. Magn Reson Med 2017;77(1):374-384.
9. Deniz CM, Carluccio G, Collins C. Parallel transmission RF pulse design with strict temperature constraints. NMR Biomed 2017;30(5):e3694-n/a.
10. Gras V, Boland M, Vignaud A, Ferrand G, Amadon A, Mauconduit F, Le Bihan D, Stöcker T, Boulant N. Homogeneous non-selective and slice-selective parallel-transmit excitations at 7 Tesla with universal pulses: A validation study on two commercial RF coils. PloS one 2017;12(8):e0183562-e0183562.
11. Malviya S, Voepel-Lewis T, Eldevik OP, Rockwell DT, Wong JH, Tait AR. Sedation and general anaesthesia in children undergoing MRI and CT: adverse events and outcomes. Br J Anaesth 2000;84(6):743-748.
12. Havidich JE, Beach M, Dierdorf SF, Onega T, Suresh G, Cravero JP. Preterm Versus Term Children: Analysis of Sedation/Anesthesia Adverse Events and Longitudinal Risk. Pediatrics 2016;137(3):e20150463.
13. Mallory MD, Travers C, McCracken CE, Hertzog J, Cravero JP. Upper Respiratory Infections and Airway Adverse Events in Pediatric Procedural Sedation. Pediatrics 2017;140(1).
14. Boriosi JP, Eickhoff JC, Klein KB, Hollman GA. A retrospective comparison of propofol alone to propofol in combination with dexmedetomidine for pediatric 3T MRI sedation. Paediatr Anaesth 2017;27(1):52-59.
15. Schwarz ST, Afzal M, Morgan PS, Bajaj N, Gowland PA, Auer DP. The 'swallow tail' appearance of the healthy nigrosome - a new accurate test of Parkinson's disease: a case-control and retrospective cross-sectional MRI study at 3T. PLoS One 2014;9(4):e93814.
16. Prasher V, Cumella S, Natarajan K, Rolfe E, Shah S, Haque MS. Magnetic resonance imaging, Down's syndrome and Alzheimer's disease: research and clinical implications. J Intellect Disabil Res 2003;47(Pt 2):90-100.
17. Shao Y, Zeng P, Wang S. Statistical simulation of SAR variability with geometric and tissue property changes by using the unscented transform. Magn Reson Med 2015;73(6):2357-2362.
18. Le Garrec M, Gras V, Hang MF, Ferrand G, Luong M, Boulant N. Probabilistic analysis of the specific absorption rate intersubject variability safety factor in parallel transmission MRI. Magn Reson Med 2017;78(3):1217-1223.
19. Murbach M, Zastrow E, Kuster N. Virtual Population Based Correlations between B1+, Whole-Body and Local SAR. 2018; Paris, France. p 4391.
20. Kozlov M, Turner R. Effects of tuning condition, head size and position on the SAR of MRI dual-row transmit arrays. 2013 6-10 Oct. 2013. p 708-711.
21. Kopanoglu E. Near real-time parallel-transmit pulse design. 2018; Paris, France. p 3392.
Figures