3138
Dilatation of Virchow-Robin Spaces is An Acute Phase Response in Children with Epileptic Seizure1Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China, 2Xi’an AccuRad Network and Technology Co.Ltd., Xi’an, China, 3Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Life Science and Technology, Xi’an Jiao tong University, Xi’an, China
Synopsis
Dysfunction of Virchow -Robin spaces (VRS) has become an exciting avenue of research for the exploration of the pathophysiology involving CNS neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory disorders. To investigate the pathophysiological link of the dilated VRS (dVRS) in children with epilepsy, we conducted semiquantitative and quantitative assessment of dVRS visible on standard 3.0T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in children with clinical history of symptomatic generalized tonic clonic, clonic or myoclonic seizures. Our results revealed the tendency of increased number of dVRS in the early phase following epileptic seizure, suggesting that dilated VRS might be related to the cascade of immune response during epileptic seizures.
Introduction
Childhood epilepsy has become a major problem imposes acute and long-lasting effects on the developing brain[1]. Recent studies have found neuroinflammation play a major role in the pathophysiology of epilepsy[2]. Virchow Robin spaces play an essential role in generation and maintenance of inflammatory response in the brain. Dysfunction of VRS has become an interesting component in the central nervous system (CNS) pathophysiology. Quantification of dVRS has been extensively applied in several neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders [3,4]. However, there are few studies of dVRS in epilepsy [5-7].Therefore, this study aims to assess the quantification of dVRS visible on standard MRI and investigate their correlation with epileptic seizuresMethods
Participants: Our study included 36 epileptic children (age range 1-12 years) with clinical history of symptomatic generalized tonic clonic, clonic or myoclonic seizures, compared with 30 control groups of matched age and sex who underwent 3.0T MRI examination in our institution between 2015 and 2017. Data and statistical analysis: The severity of dVRS was semiquantitatively and quantitatively evaluated in the region of centrum semiovale (CSO) and basal ganglia (BG) using T2 weighted MRI images. For semiquantitative visual assessment process, dVRS were rated 0 (none), 1 (1–10), 2 (11–20), 3 (21–40) and 4 (>40) per entire slice with maximum number in the region of BG and CSO [8,9]. (Table 1) For automated segmentation of dVRS, firstly, axially oriented T2-weighted images were processed with the aid of the FMRIB software library (FSL, www.fmrib.ox.au.uk/fsl), to eliminate the mask of white matter, cortical gray matter and ventricular CSF. Then the images were exported from FSL to custom software built in Matlab (https://www.mathworks.com) for VRS quantification. Non parametric Mann Whitney U test was used for comparing the dVRS parameters between case and control groups. The correlation between the severity of dVRS with time of seizure onset and duration were compared using bivariate Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient analysis.Results
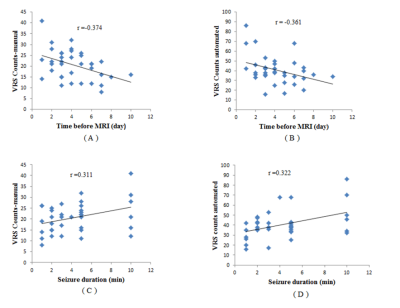
Both semiquantitative and automated quantitative methods showed good agreement (p = 0.047) in supporting our hypothesis. Inter-rater and intra-rater reliability of our visual rating score were excellent, Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) for epileptic patients were (ICC = 0.995, CI 0.991- 0.997) and (ICC = 0.997, CI 0.995 - 0.998) respectively and for control group were (ICC = 0.954, CI 0.922- 0.972) and (ICC = 0.998, CI 0.997- 0.999) respectively. The severity of dVRS was significant higher in the region of white matter in epilepsy compared to control group in both methods (p < 0.001). (Table 1and 2)There was an increase in the number of dVRS in the acute phase following seizure onset which was found to decrease significantly with time (p =0.031). There was also a slight increase trend of the severity of dVRS with seizure duration even though we only found marginally statistical significant at the 5% level (Spearman’s rho = 0.322, p = 0.056).Discussion
Our study provide the evidence to support the notion that dilatation of VRS might be associated with seizure activities, we found a significant difference between the severity of dVRS in epileptic children compare to control in the region of centrum semiovale (p <0.001). High prevalence of dVRS in the region of white matter has been strongly associated with neuroinflammatory and neurodegerative disorders[4]. The main strength of our study in comparison to previous studies is based on the established correlation between epileptic seizure and dilatation of Virchow robin spaces. In our study, we observed increased number of dVRS in the acute phase following seizure onset which were found to show a decreasing trend over period of time (figure 1). These observations showed the active participation of VRS in the immune response chain during epileptic seizure. These findings are in consistence with other acute inflammatory biomarkers of epilepsy, established by serum immune mediators [10] and histopathology studies [11]. Both manual and automated method showed identical accuracy in supporting our hypothesis. However, there were a slight higher number of dVRS counts when using automated segmentation (figure 2), suggesting that the method of quantification employed by automated software can apparently detect more dVRS and may improve precision of dVRS counting compared with visual methods. Accurate and precise quantification of dVRS are essential for both reliability and reproducibility.Conclusion
Our study revealed higher severity of dVRS in the epilepsy group. The increased number of dVRS was more prominent in the early phase following epileptic seizure.Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0100300), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81471631, 81771810 and 81171317), the 2011 New Century Excellent Talent Support Plan of the Ministry of Education, China (NCET-11-0438), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (xjj2018265), the Fundamental Research Funds of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University (2017QN-09).References
Koh S. Role of Neuroinflammation in Evolution of Childhood Epilepsy[J]. J Child Neurol, 2018, 33 (1): 64-72. Vezzani A, French J, Bartfai T, et al. The role of inflammation in epilepsy[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2011, 7 (1): 31-40. Ramirez J, Berezuk C, McNeely AA, et al. Imaging the Perivascular Space as a Potential Biomarker of Neurovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2016, 36 (2): 289-299. Cherian I, Beltran M, Kasper EM, et al. Exploring the Virchow-Robin spaces function: A unified theory of brain diseases[J]. Surg Neurol Int, 2016, 7 (Suppl 26): S711-S714. Afifi AK. Enlarged Virchow–Robin Spaces along the Medullary Perforators in a Child with Seizures[J]. Journal of Neuroimaging, 1996, 6 (3): 197-198. Biedroń A, Steczkowska M, Kubik A, et al. Dilatation of Virchow–Robin spaces in children hospitalized at pediatric neurology department[J]. Neurologia i Neurochirurgia Polska, 2014, 48 (1): 39-44. Feldman RE, Rutland JW, Fields MC, et al. Quantification of perivascular spaces at 7T: A potential MRI biomarker for epilepsy[J]. Seizure, 2018, 54: 11-18. Potter GM, Chappell FM, Morris Z, et al. Cerebral perivascular spaces visible on magnetic resonance imaging: development of a qualitative rating scale and its observer reliability[J]. Cerebrovasc Dis, 2015, 39 (3-4): 224-231. Maclullich AM, Wardlaw JM, Ferguson KJ, et al. Enlarged perivascular spaces are associated with cognitive function in healthy elderly men[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2004, 75 (11): 1519-1523. Alapirtti T, Lehtimaki K, Nieminen R, et al. The production of IL-6 in acute epileptic seizure: A video-EEG study[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2018, 316: 50-55. Klement W, Garbelli R, Zub E, et al. Seizure progression and inflammatory mediators promote pericytosis and pericyte-microglia clustering at the cerebrovasculature[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2018, 113: 70-81.Figures