2197
DANTE-Prepared FLASH: Three-Dimensional Vessel Wall Imaging Of ApoE-/- Mouse at 7 Tesla1School of Biomedical Engineering, Guangdong Provincial Key Laborary of Medical Image Processing, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, People's Republic of China, Guangzhou, China, 2Department of Pathophysiology, Key Lab for Shock and Microcirculation Research of Guangdong, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, 510515, PR China, Guangzhou, China, 3Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China, Guangzhou, China, 4Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Basic Sciences, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China
Synopsis
There is a growing preclinical demand for methods to characterize atherosclerotic plaque in vivo. Recently proposed DANTE for dark-blood preparation successfully in vessel wall imaging. However, previous studies were performed at 3T and used for vessel wall imaging of human. It remains unclear that if DANTE module could be used for apoE-/- mouse at 7T. Here we demonstrated a sequence using DANTE dark-blood preparation combined with FLASH readout (DANTE-FLASH) for three-dimensional (3D) vessel wall imaging at 7 Tesla (T).
Introduction
There is a growing preclinical demand for methods to characterize atherosclerotic plaque in vivo1. Recent studies have introduced a novel application of DANTE pulse trains to the suppression of signal from moving spins, while largely preserving the signal from static spins2. It demonstrates successfully in vessel wall imaging3-5. However, previous studies were performed at 3T and used for vessel wall imaging of human. Pre-clinical MRI characterization of an apoE-/- mouse model of carotid artery atherosclerotic plaques is very challenging, due to the small dimensions of vessels, high heart rate, and rapid blood flows. It remains unclear that if DANTE module could be used for apoE-/- mouse at 7T. Here we demonstrated a sequence using DANTE dark-blood preparation combined with FLASH readout (DANTE-FLASH) for three-dimensional (3D) vessel wall imaging at 7 Tesla (T).Methods
Image sequence: The sequence was composed of DANTE module, spoiler gradients, 3D FLASH readout, and extra magnetization recovery (Figure1). A DANTE module for dark-blood preparation consists of a series of low-flip-angle RF pulses interspersed with unipolar dephasing gradients which are simultaneously applied on all axes. For the purpose of maximizing dark-blood effects, centric phase-encoding ordering was employed in FLASH readout. In vivo study, a constant TR was used to adjust the time for extra magnetization recovery and for other modules.
Image acquisition: This study was approved by local institutional review board. Two 8 weeks old ApoE-/- mice were fed with a high-fat diet for approximately 20 weeks. Mice underwent MR scan using Bruker 7T MRI scanner. The parameters for the DANTE module included: flip angle :15°, pulse train length :150, inter-pulse duration td: 0.91 ms. The parameters for the FLASH readout included: echo spacing: 12.30 ms, TE: 4.34 ms, flip angle : 8°,field of view: 20×20×8 mm3, turbo factor: 21, spatial resolution: 0.078×0.078×0.2 mm,number of averages: 4. TR: 1400 ms.
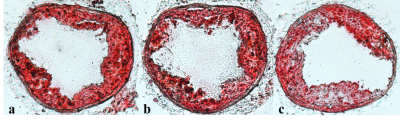
Histology: Two days after MRI measurements, histologic sections were made. Carotid artery was sectioned into 10-µm serial sections perpendicular to the vessel direction. Sections were stained with Hematoxylin, Oil Red O for lipids6.
Results
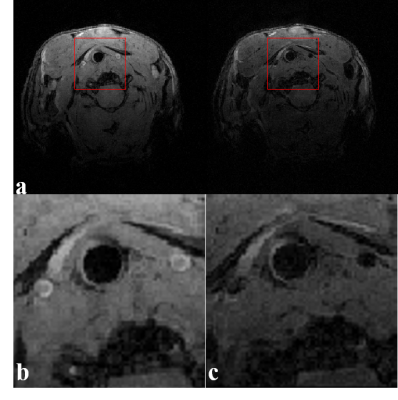
All mouse successfully completed the MR scans. As compared with figures acquired without DANTE (Figure 2(a),left), the signal from flowing blood was suppressed and plaque was clearly visible in those figures acquired with DANTE-FLASH under the same imaging parameters (Figure 2(a),right).Partial enlarged drawings are separately shown (Figure 2(b),Figure 2(c)). To confirm the existence of carotid artery plaque, apoE-/- mouse were evaluated by histology, as shown in (Figure 3). MRI Images agree well with histological sections.Discussion
In this work, the DANTE module is combined with the FLASH readout to achieve high spatial resolution carotid artery imaging at 7T. The feasibility of using the technique to characterize the carotid artery atherosclerotic plaques of an apoE-/- mouse model was successfully confirmed. Previous studies suggested that DANTE module is flow insensitivity for dark-blood preparation[1], making it suitable for flow signal suppression even if the blood flow is rather fast in the carotid artery of apoE-/- mouse. There are two limitations in this work. Frist, the DANTE module suppresses the signal of flow blood as well as the signal of static tissues. To minimize attenuation of static spins and substantial attenuation of flowing spins, the parameters of DANTE-FLASH need to be further optimized. Second, only two mice were used in our experiments to prove the feasibility of this technique. To evaluate novel treatment strategies, large population of mice studies will be our future work.Conclusion
Our results indicate that 3D DANTE-FLASH is suitable for characterizing the carotid artery atherosclerotic plaques of an apoE-/- mouse model at 7T. Future studies will focus on development of accurate quantification of atherosclerotic plaques and evaluate novel treatment strategies in the pre-clinical MRI protocols.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Blackwell GG, Pohost GM. The evolving role of MRI in the assessment of coronary-artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1995;75:74D–78D.
2.Li L, Miller KL, Jezzard P. DANTE-prepared pulse trains: a novel approach to motion-sensitized and motion-suppressed quantitative magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 2012;68: 1423–1438
3.Xie G, Zhang N, Xie Y, et al. DANTE-prepared three-dimensional FLASH: A fast isotropic-resolution MR approach to morphological evaluation of the peripheral arterial wall at 3 Tesla[J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2016, 43(2):343-351.
4. Li L, Chai JT, Biasiolli L, Robson MD, Choudhury RP, Handa AI, Near J, Jezzard P. Black-blood multicontrast imaging of carotid arteries with DANTEprepared 2D and 3D MR imaging. Radiology. 2014;273:560–9.
5.Xie Y, Yang Q, Xie G, Pang J, Fan Z, Li D. Improved black‐blood imaging using DANTE‐SPACE for simultaneous carotid and intracranial vessel wall evaluation. Magn Reson Med. 2016;75:2286–94.
6.van Bochove G S, Straathof R, Krams R, et al. MRI-determined carotid artery flow velocities and wall shear stress in a mouse model of vulnerable and stable atherosclerotic plaque.[J]. Magnetic Resonance Materials in Physics Biology & Medicine, 2010, 23(2):77-84.